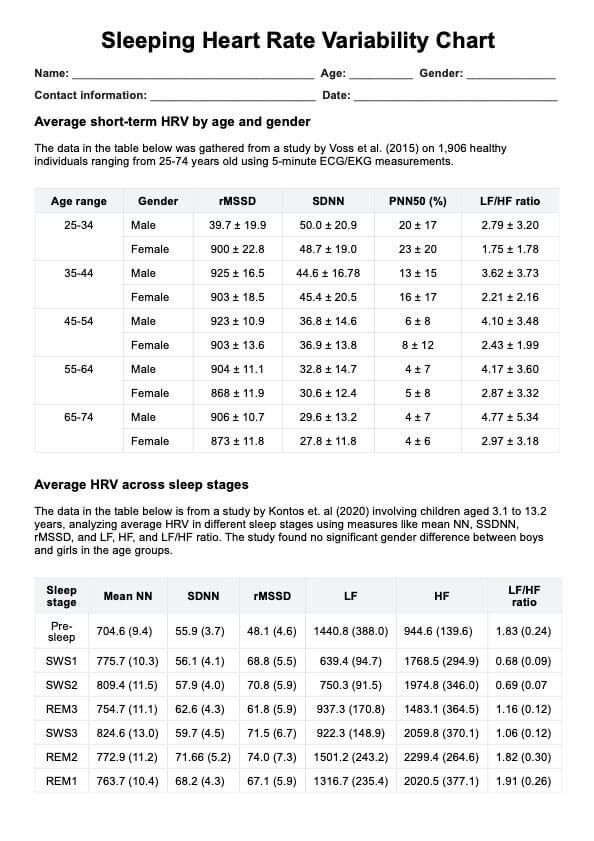
A good HRV range during sleep varies, but in general, a higher HRV indicates better sleep quality and overall health. The HRV range for each sleep stage can differ based on individual factors such as age and health status.
Use our template to track your patient's sleeping heart rate variability and gain insight into their heart health.
A good HRV range during sleep varies, but in general, a higher HRV indicates better sleep quality and overall health. The HRV range for each sleep stage can differ based on individual factors such as age and health status.
Healthy HRV scores vary by age. For example, younger adults typically have higher HRV compared to older adults. Using age-specific HRV ranges, such as those in our chart, can provide insight into whether your HRV is within a healthy range.
Low HRV might be a sign of stress, poor cardiovascular health, or sleep disturbances. While a single low HRV reading isn’t always cause for concern, consistently low HRV may warrant further investigation by a healthcare professional.
EHR and practice management software
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments