Understanding student risk
Student risk refers to the presence of behaviors or conditions that put a student at a higher likelihood for adverse outcomes, such as academic failure, delinquency, or mental health problems. These risks can manifest in various forms, including externalizing and internalizing behaviors.
Internalizing behavior refers to the tendency to turn emotional distress inward, leading to symptoms like sadness, withdrawal, and anxiety. This can include specific disorders such as major depressive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder (Chou et al., 2015).
On the other hand, externalizing behaviors involve acting out or displaying disruptive behaviors towards others. These may include aggression, hyperactivity, and attention problems.
Both internalizing and externalizing behaviors can significantly impact a student's academic performance, social relationships, and overall well-being.
Mental disorders, including anxiety disorders and depressive disorders, are some of the most common mental health issues among children and adolescents. According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM), childhood anxiety disorders affect around 25% of children and adolescents. In comparison, approximately 5% of young people struggle with depressive disorders (Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, 2016).
Separation anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, and panic disorder are among the most prevalent childhood anxiety disorders. These conditions can significantly impair a child's ability to function in school and other areas of life. Additionally, they may also co-occur with depressive symptoms or disorders.
Risk factors for developing internalizing disorders can include genetics, environmental stressors, and traumatic events. Children who experience adverse childhood experiences, such as abuse or neglect, are also at a higher risk for developing internalizing disorders (Parenting For Brain, n.d.).
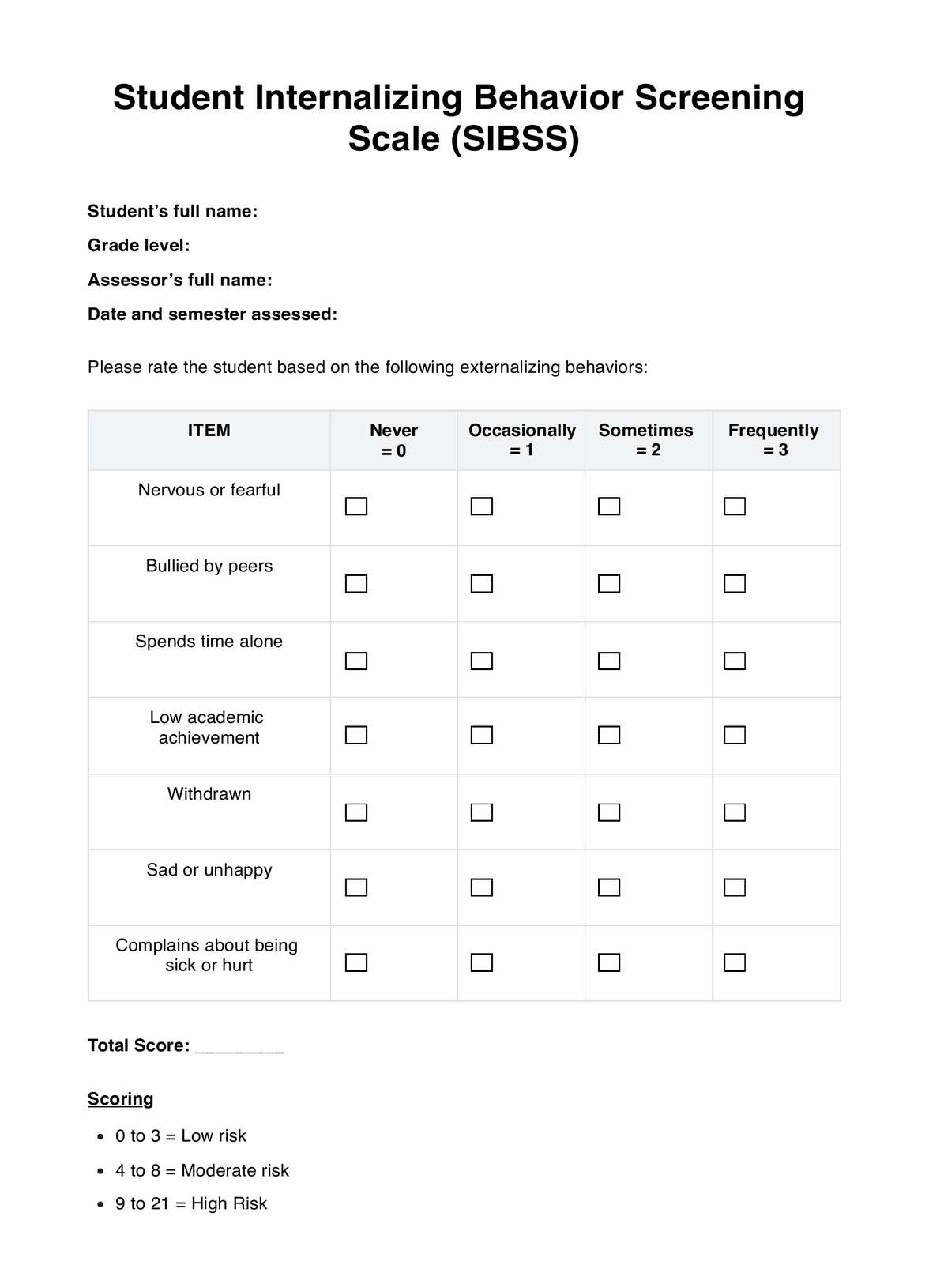
Printable Student Internalizing Behavior Screening Scale (SIBSS)
Download this Student Internalizing Behavior Screening Scale (SIBSS) to assess if students are at risk.