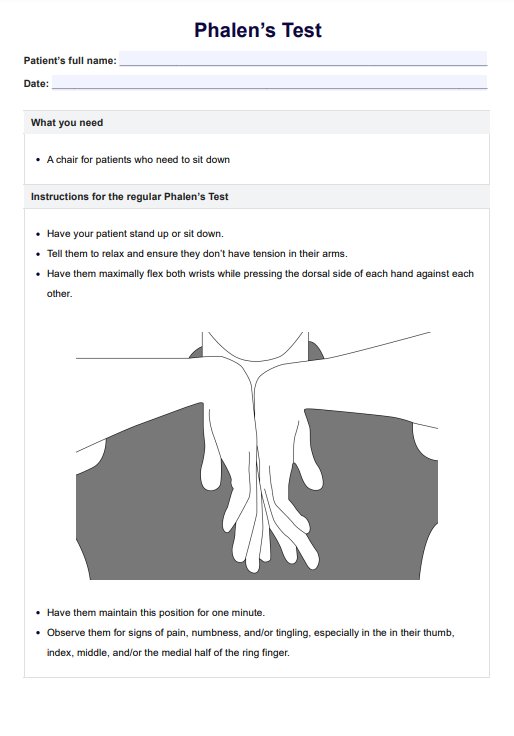
The Phalen's Test was developed by George S. Phalen, an American orthopedic surgeon and professor, in the 1950s. He initially used the assessment to diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome in patients, but it has since been adapted for other nerve-related conditions.
Phalen's Test
Learn about Phalen's Test and include it in your clinical tests for diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome!
Use Template
Phalen's Test Template
Commonly asked questions
The Phalen's Test can evaluate the median nerve for signs of compression and rule out carpal tunnel syndrome. It can also accurately diagnose other nerve-related conditions and assess the effectiveness of treatments.
The Phalen's Test is used to evaluate the median nerve for signs of compression and determine whether a patient has carpal tunnel syndrome or other nerve-related issues.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











