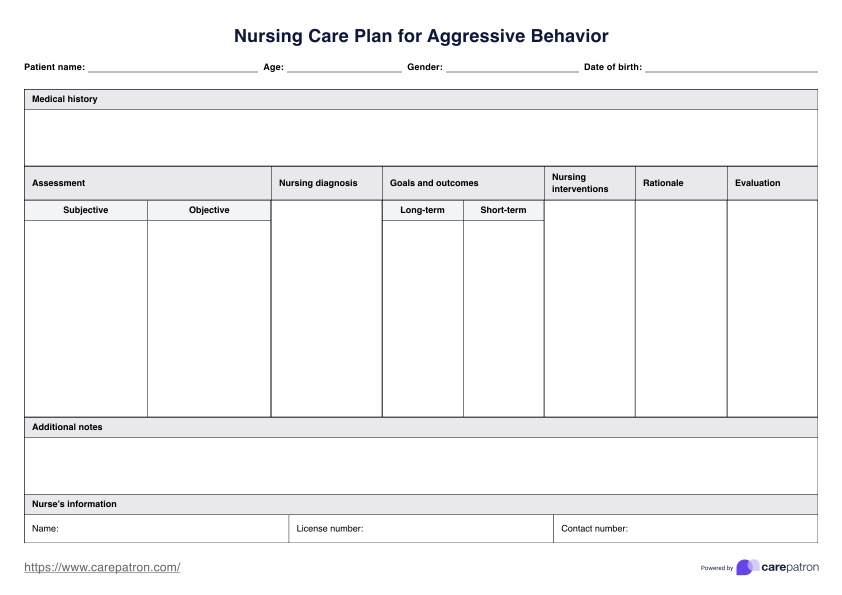
What is a Nursing Care Plan for Aggressive Behavior?
Managing aggressive behavior in nursing requires a comprehensive approach beyond merely controlling outbursts. A Nursing Care Plan for Aggressive Behavior addresses the root causes of unacceptable behavior while ensuring the safety and well-being of everyone involved. By understanding the triggers, interventions can be tailored to promote positive change and reduce the risk of harm to the patient and others.
Such a plan provides a structured approach for healthcare professionals to respond effectively, fostering a safer, more therapeutic environment that supports the patient's emotional needs. It also ensures consistency in care, builds trust, and improves the patient's overall well-being. In extreme cases, de-escalation techniques and safety measures may be necessary, but they are used alongside efforts to address underlying issues. Education plays a vital role as patients learn the impact of their actions and develop tools for managing stress. At the same time, caregivers gain the knowledge needed to create a supportive environment essential for recovery.