What is a hematocrit test?
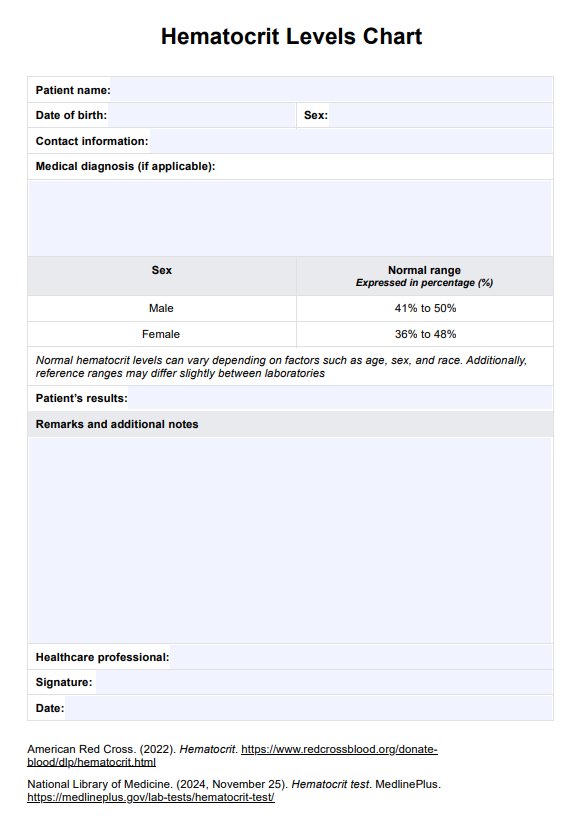
A hematocrit test, often called an HCT, is a common blood test that measures the percentage of red blood cells (RBCs) in a person's blood. It is a vital component of a complete blood count (CBC), a standard diagnostic test performed for various medical purposes, including routine check-ups, disease diagnosis, and monitoring the progress of certain medical conditions.
This simple blood test provides valuable information about a person's blood's overall health and oxygen-carrying capacity. The bone marrow produces red and white blood cells. Hemoglobin, proteins in red blood cells, carry oxygen from the lungs to various tissues and organs throughout the body. Therefore, the hematocrit level reflects the blood's ability to deliver oxygen efficiently.
It is conducted by taking a small blood sample, typically from a vein in the arm, and then placing it in a centrifuge machine that rapidly spins the blood to separate its components. As the blood cells settle, they split into layers, with red blood cells sinking to the bottom due to their density. The hematocrit value is calculated as the ratio of the volume of red blood cells to the total blood volume sample, expressed as a percentage.