A torn trapezius can heal on its own with proper rest, but recovery depends on the severity of the injury. Mild to moderate tears may improve with ice therapy, gentle stretching, and strengthening exercises to restore muscle function around the posterior aspect of the neck and shoulder blades. However, severe tears may require medical intervention to prevent complications like a pinched nerve or chronic neck pain.
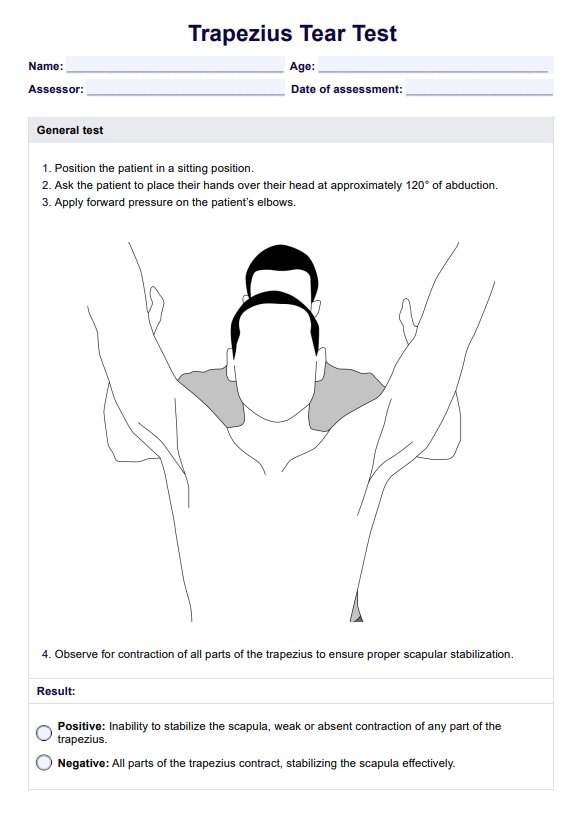
Trapezius Tear Test
Learn about trapezius tears and strains, their symptoms, causes, and how to use our Trapezius Tear Test template.
Trapezius Tear Test Template
Commonly asked questions
A trapezius strain is a mild overstretching of the muscle, causing neck pain and stiffness. A tear involves actual damage to muscle fibers, leading to more intense pain and possible weakness in the shoulder blades and posterior aspect of the upper back. Strains typically recover faster, whereas tears may take longer and pose a higher risk of affecting muscle function or irritating a pinched nerve.
To test trapezius muscle function, clinicians use a resisted shoulder shrug test to check for weakness or neck pain, and a resisted shoulder abduction test to assess muscle strength near the shoulder blades. Palpation and range of motion tests help identify tenderness in the posterior aspect of the neck. If nerve involvement or a pinched nerve is suspected, imaging or EMG may be required.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











