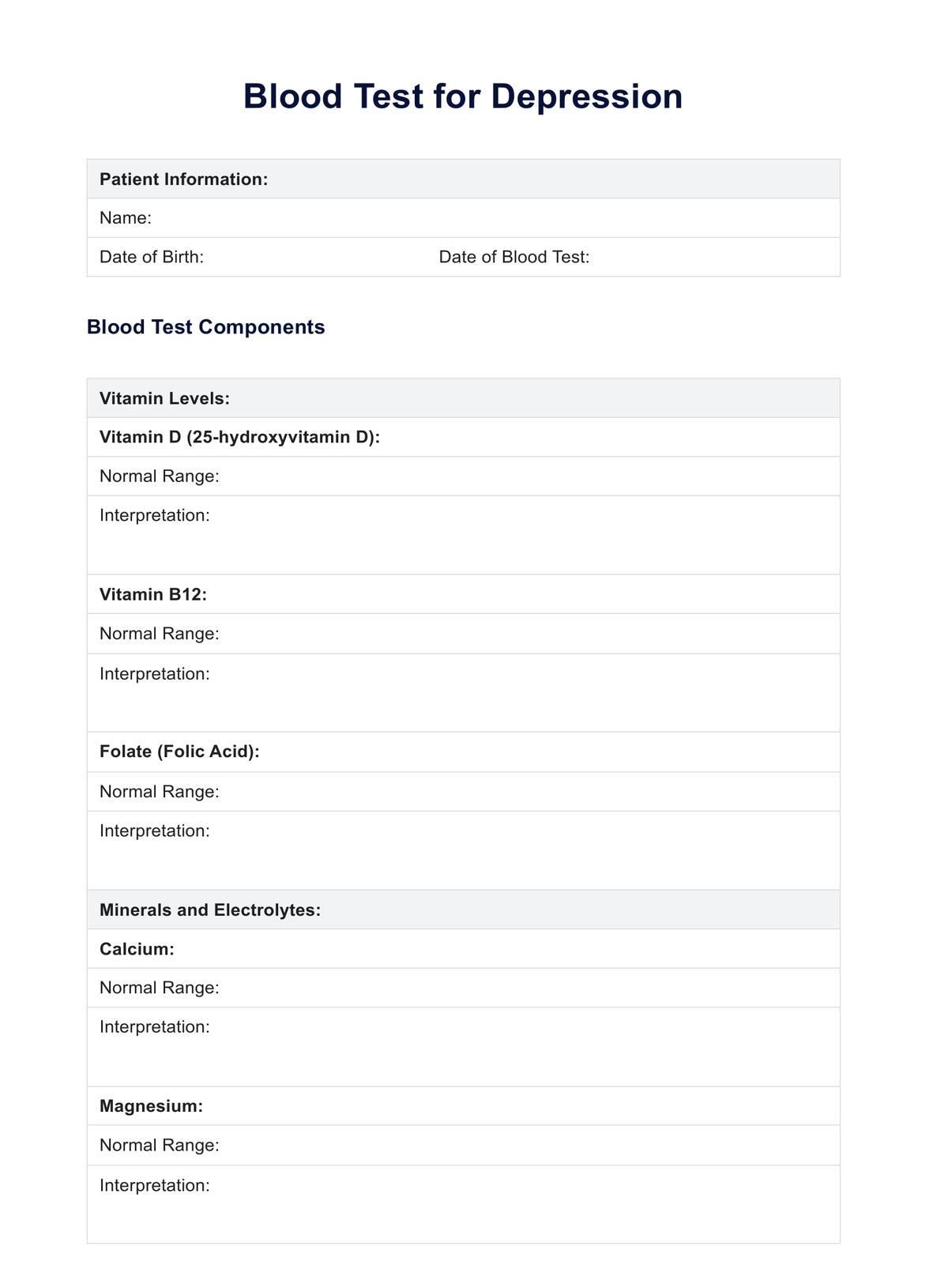
While there is no specific blood test for diagnosing depression, certain blood tests can provide valuable information. Assessing vitamin levels, thyroid function, and ruling out other medical conditions through blood tests can contribute to a comprehensive mental health assessment.
Blood Test for Depression
Learn about blood tests for depression and download Carepatron's free example in PDF format to understand the process better.
Blood Test for Depression Template
Commonly asked questions
The gold standard for diagnosing depression is a thorough clinical assessment by a mental health professional. Tools like the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale are commonly used, complemented by discussions about symptoms, medical history, and potential contributing factors.
Conditions often associated with depression include anxiety disorders, chronic pain conditions, and other mood disorders like bipolar disorder. Addressing these coexisting conditions is crucial for comprehensive depression management.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











