Mental health professionals consider several factors, including the type and severity of the mental health condition, the patient's health history, and potential side effects, to decide the most appropriate medication.
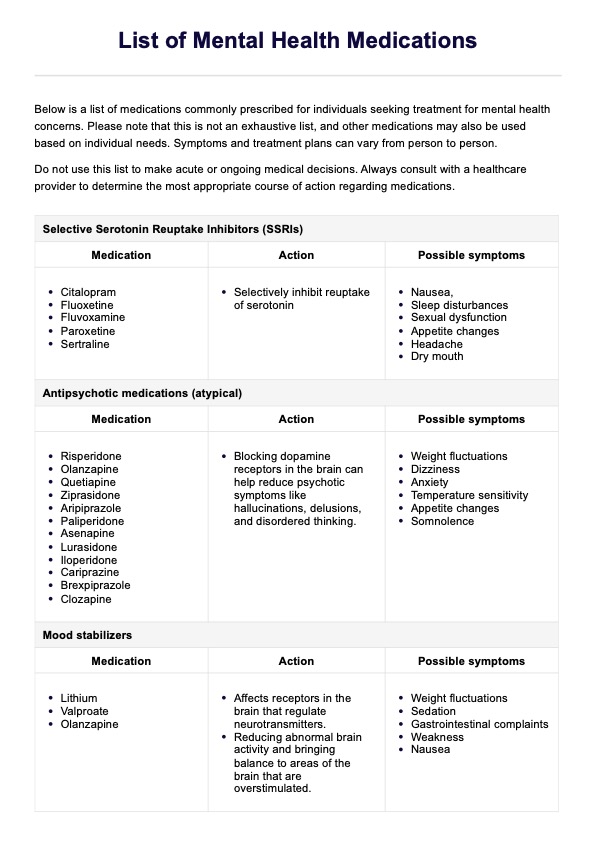
List of Mental Health Medications
Download our free List of Mental Health Medications PDF template. Learn about common medications, their uses, benefits, and more in this easy-to-use guide.
Use Template
List of Mental Health Medications Template
Commonly asked questions
While mental health medications can significantly improve symptoms, they are typically part of a broader treatment plan that may include therapy and lifestyle changes.
Sometimes, like all medications, mental health medications may have side effects. It's important to discuss these potential side effects with a healthcare provider.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











