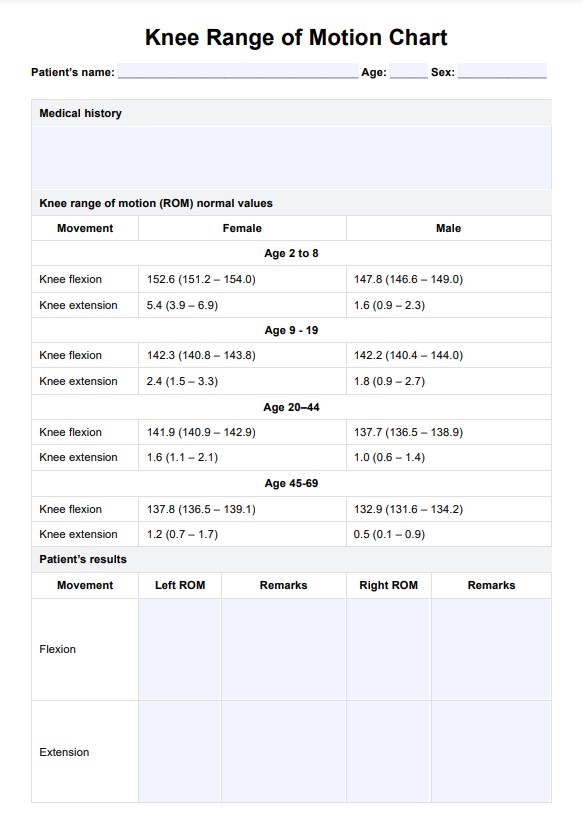
You can use the knee range of motion chart template as a document where you can record results from your assessments or examinations.
Knee Range of Motion Chart
Utilize a knee range of motion chart to assess your patient's knee joint range and capabilities. Click here for a free template copy!
Use Template
Knee Range of Motion Chart Template
Commonly asked questions
Orthopedists and orthopedic surgeons are the ones who will benefit the most from using the knee range of motion chart template.
Having a normal range of motion in the knee is important to perform daily activities such as walking or climbing stairs without difficulty or limitations.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











