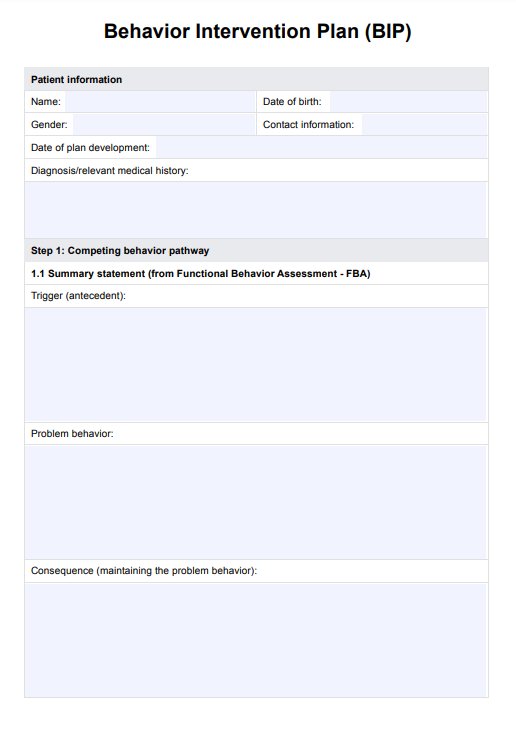
An example of a Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) is a plan designed to address a student's disruptive behavior in the classroom. It includes targeted interventions, such as teaching a replacement behavior, setting clear consequences, and tracking progress to ensure positive behavior changes.
Behavior Intervention Plan
Learn about Behavior Intervention Plans (BIP) and download Carepatron's free PDF template to streamline behavior management and track progress effectively.
Behavior Intervention Plan Template
Commonly asked questions
The seven components of an effective Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) include: developing a competing behavior pathway, identifying intervention strategies, recognizing consequence strategies, creating a safety plan, establishing an implementation plan, developing a monitoring and evaluation plan, and identifying generalization and maintenance strategies.
An Individualized Education Plan (IEP) is a legally binding document that outlines specific educational goals for students with disabilities, while a Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) focuses on addressing specific behavioral challenges. The BIP can be part of an IEP, but it specifically targets behavior management strategies.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











