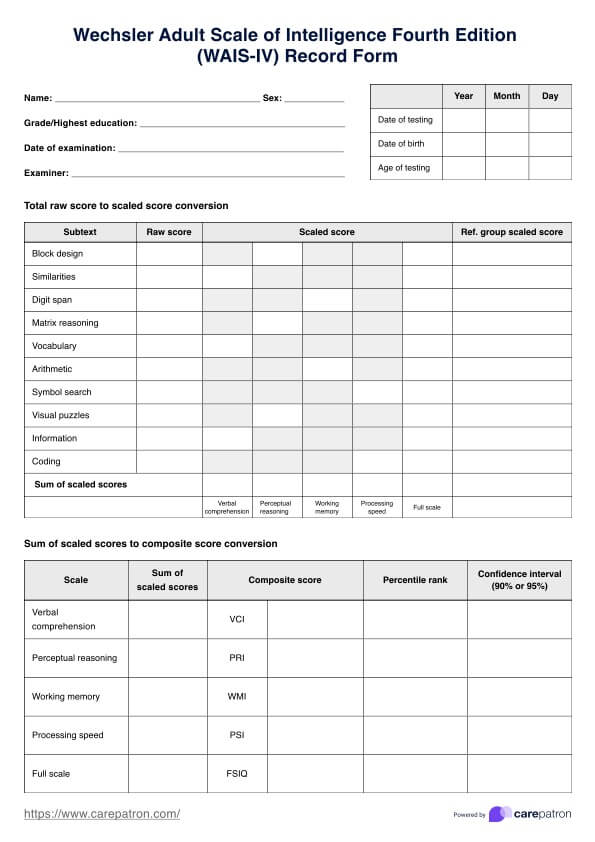
The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale—Fourth Edition (WAIS-IV) measures cognitive abilities in adults aged 16 to 90. It evaluates four key domains of intelligence: Verbal Comprehension, Perceptual Reasoning, Working Memory, and Processing Speed. The test assesses verbal skills, problem-solving, spatial reasoning, and processing speed, providing a comprehensive measure of cognitive ability.
WAIS-IV
Learn about WAIS-IV, a comprehensive intelligence test for adults. Understand its structure and scoring methods for insightful assessments.
WAIS-IV Template
Commonly asked questions
The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale—Fourth Edition (WAIS-IV) average IQ score is 100. This fixed score serves as a reference point for comparing individual scores. Approximately two-thirds of all scores fall between 85 and 115, with scores below 70 generally considered to be in the intellectually disabled range.
The 10 core subtests of the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale—Fourth Edition (WAIS-IV) are Arithmetic, Block Design, Comprehension, Digit Span, Digit Symbol, Information, Letter-Number Sequencing, Matrix Reasoning, Picture Arrangement, and Vocabulary. These subtests are used to obtain an overall score and provide scores for the four Index Scores: Verbal Comprehension, Perceptual Reasoning, Working Memory, and Processing Speed.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











