Normal IgE levels vary, typically from 3 to 423 IU/mL for adults. They are measured using a blood test, which assesses total IgE in the serum. This test is crucial for diagnosing allergic diseases and understanding the immune system's response to allergens. The normal range can differ slightly depending on the laboratory's reference intervals.
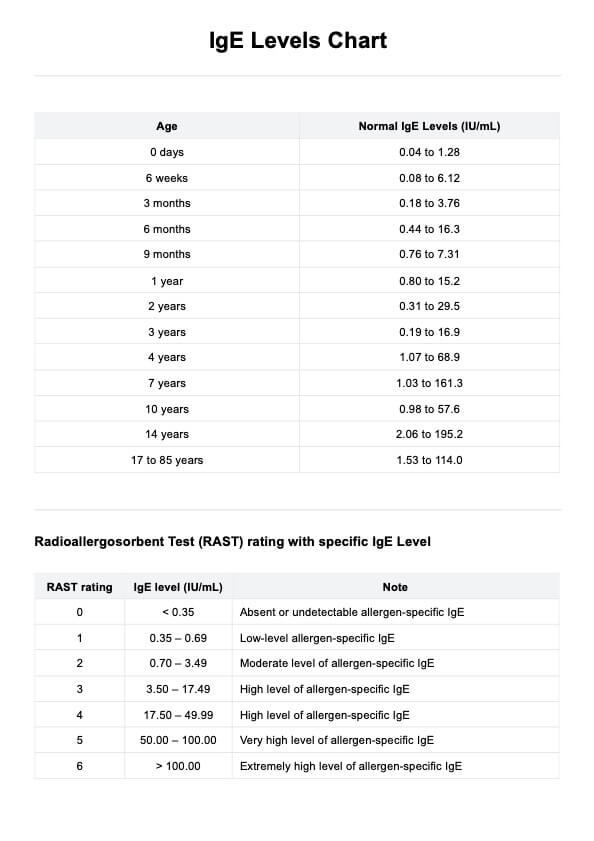
IgE Levels Chart
IgE Levels Chart: Comprehensive visual guide detailing normal and allergen-specific IgE levels by age, from newborns to adults, including RAST ratings.
IgE Levels Chart Template
Commonly asked questions
Elevated IgE levels are often associated with allergic reactions and atopic diseases like atopic dermatitis. IgE, or Immunoglobulin E, plays a crucial role in hypersensitivity reactions, where the immune system overreacts to specific allergens, leading to symptoms like itching, redness, and swelling.
Yes, allergy blood testing, which includes measuring specific IgE levels against certain allergens, can identify what you might be allergic to. These tests help diagnose allergies, including food and allergic asthma, by detecting IgE molecules specific to different allergens.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











