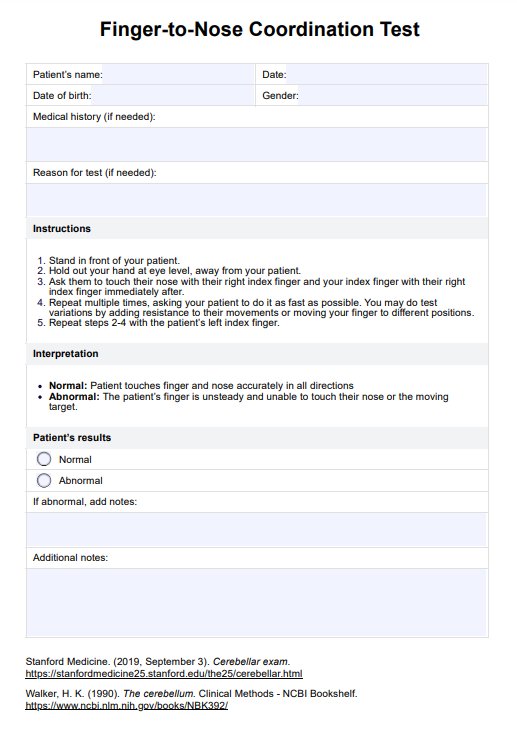
It tests cerebellar function and how it's affecting the person's coordination and equilibrium.
Finger-to-Nose Coordination Test
Learn more about the Finger-to-Nose Coordination Test and when to use it. Click here for more information on the test and a free template of the test's instructions.
Use Template
Finger-to-Nose Coordination Test Template
Commonly asked questions
It's considered positive or abnormal if the person has a tremor in the arm with cerebellar damage while doing the test.
It's as simple as asking the patient to touch their nose and then touch their finger with the index finger of the arm being tested.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











