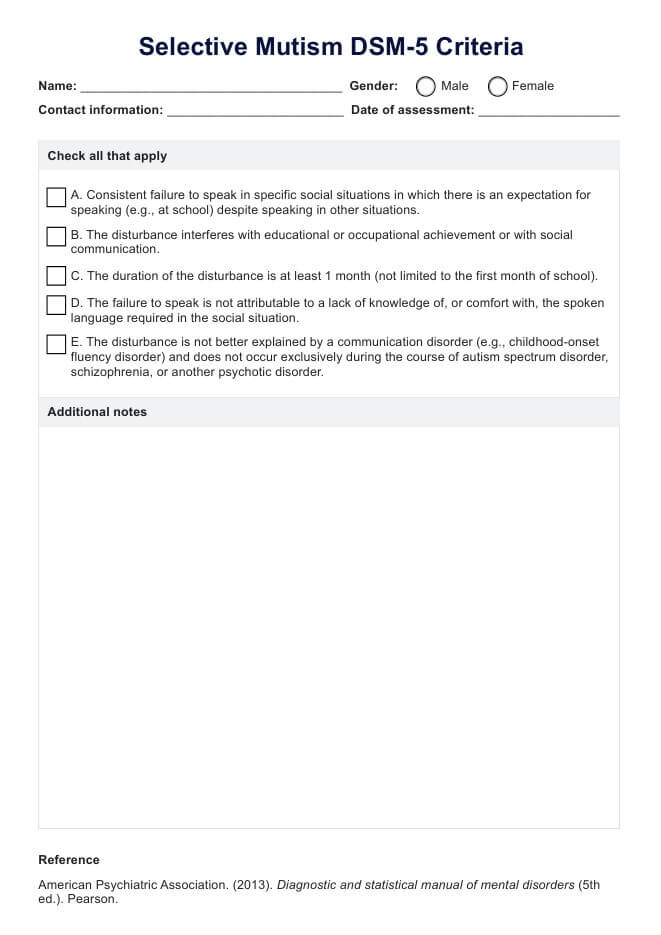
The diagnostic process typically involves clinical interviews with the child, parents, and teachers, behavioral observations across different settings, standardized assessments, language evaluations, and social skills and emotional functioning assessments.
Selective Mutism DSM-5 Criteria
Understand Selective Mutism DSM-5 Criteria with our handy resource. Download a PDF copy here.
Selective Mutism DSM-5 Criteria Template
Commonly asked questions
It is crucial to differentiate selective mutism from other conditions like autism spectrum disorder, communication disorders, and social anxiety disorder. The symptoms must persist for at least one month and interfere with educational, occupational, or social functioning. The failure to speak should not be due to a lack of knowledge of the required language or occur exclusively during other mental health conditions.
Traumatic mutism involves the complete inability to speak in all situations following a traumatic event, whereas trauma-induced selective mutism involves the inability to speak in certain situations that are reminiscent of the trauma, while the individual can still speak in other settings. Selective mutism, as an anxiety disorder, maybe a consequence of difficulty processing trauma, but it is not exclusively caused by trauma.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











