Many chronic illnesses can be prevented or their onset delayed through healthy lifestyle choices such as maintaining a healthy diet, monitoring health statistics, exercising regularly, not smoking, and moderating alcohol consumption.
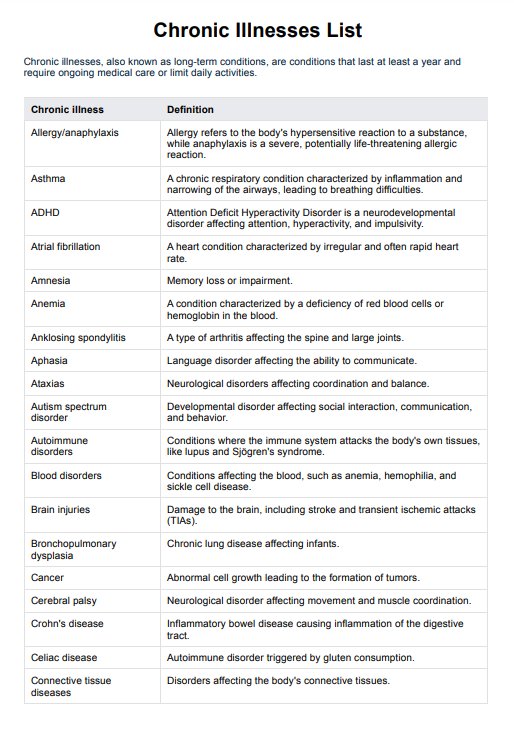
Chronic Illnesses List
Access our Chronic Illnesses List you can refer to when working on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment planning.
Chronic Illnesses List Template
Commonly asked questions
While some chronic illnesses can be managed and controlled very effectively, many conditions considered chronic do not have a cure. Treatment usually focuses on managing symptoms, improving quality of life, and preventing complications.
Chronic illnesses can impact daily life in numerous ways, including physical limitations, managing medication or treatment schedules, financial stress due to medical expenses, and emotional stress related to living with a long-term condition.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











