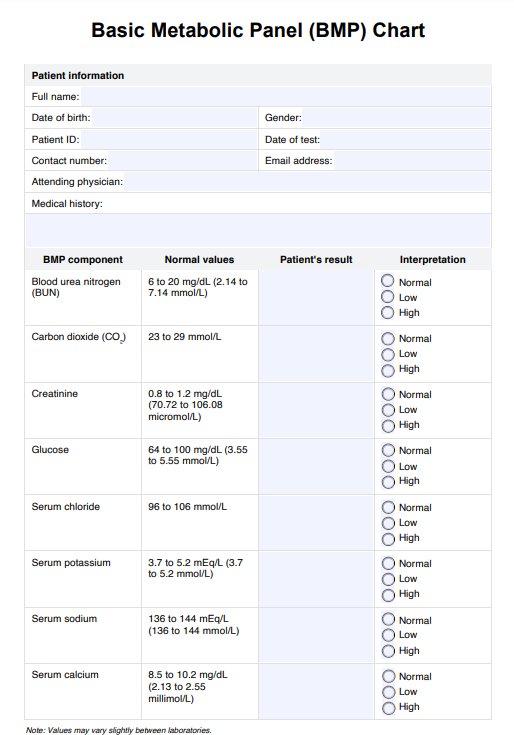
What do the results mean?
Normal ranges of the following substances indicate healthy metabolic function, while abnormal results may indicate medical complications that warrant further investigation. Note that 'normal' reference ranges may vary depending on the laboratory. Here are what BMP test results mean:
Glucose
A healthy glucose level should sit between 64 to 100 mg/dL (provided the patient fasted for the appropriate period before the blood draw).
A low glucose level may indicate hypoglycemia. If it sits above this range, hyperglycemia may be present. Patients with poorly managed diabetes or blood sugar-spiking medications may present with a high glucose level in the BMP.
Calcium
The parameters for typical calcium levels are 8.5 to 10.2 mg/L.
Low calcium levels, or hypocalcemia, are tied to the functioning of the parathyroid gland and vitamin D intake. Poor vitamin D intake can affect the patient's ability to absorb calcium. A high level of calcium present on the BMP, or hypercalcemia, may be caused by an overactive parathyroid gland. Hypercalcemia indicates a need to monitor the patient's renal status, as there is an increased risk of developing kidney stones.
Sodium
Typical sodium levels are represented by 136 to 144 mEg/L.
Hypernatremia may be a sign of dehydration and poor renal functioning. Hyponatremia, or low sodium, on the other hand, may result from poor kidney function. Note that diuretics like thiazide may affect the kidney's ability to process sodium, and hyponatremia can also be present in patients suffering from diarrhea.
Chloride
The typical normal chloride levels are 96 to 106 mEg/L.
Hypochloremia may be present in patients with renal issues, severe lung disease, or who are on loop diuretics, as this can affect chloride absorption.
Potassium
Potassium levels in the blood should be between 3.7 and 5.2 mEg/L. A patient must stay within this range, as their potassium level can potentially change the functioning and toxicity of certain medications.
Hypokalemia, or low blood potassium levels, indicates the patient may have Cushing's syndrome or is on loop diuretics or corticosteroids. Increased potassium levels indicate renal failure or Addison's disease.
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Typical blood carbon dioxide levels range between 23 and 29 mmol/L. This key level contributes to the body's acid-base balance and is a byproduct of metabolism, presenting as bicarbonate.
Low levels of CO2 indicate acidic blood and potential acidic diabetic ketoacidosis or drug-related toxicity, such as aspirin toxicity. An increased CO2 level may be present in patients with respiratory issues, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
A typical range of BUN, the amount of nitrogen in the bloodstream indicating renal function, is between 6 and 20 mg/dL. A high BUN indicates kidney issues, and a cross-analysis with creatinine levels is essential.
Creatinine
Creatinine levels should typically be between 0.8 and 1.2 mg/dL, and this small range is due to the fact that creatinine should only exist in very small amounts in the bloodstream. High levels of creatinine indicate poor kidney function.