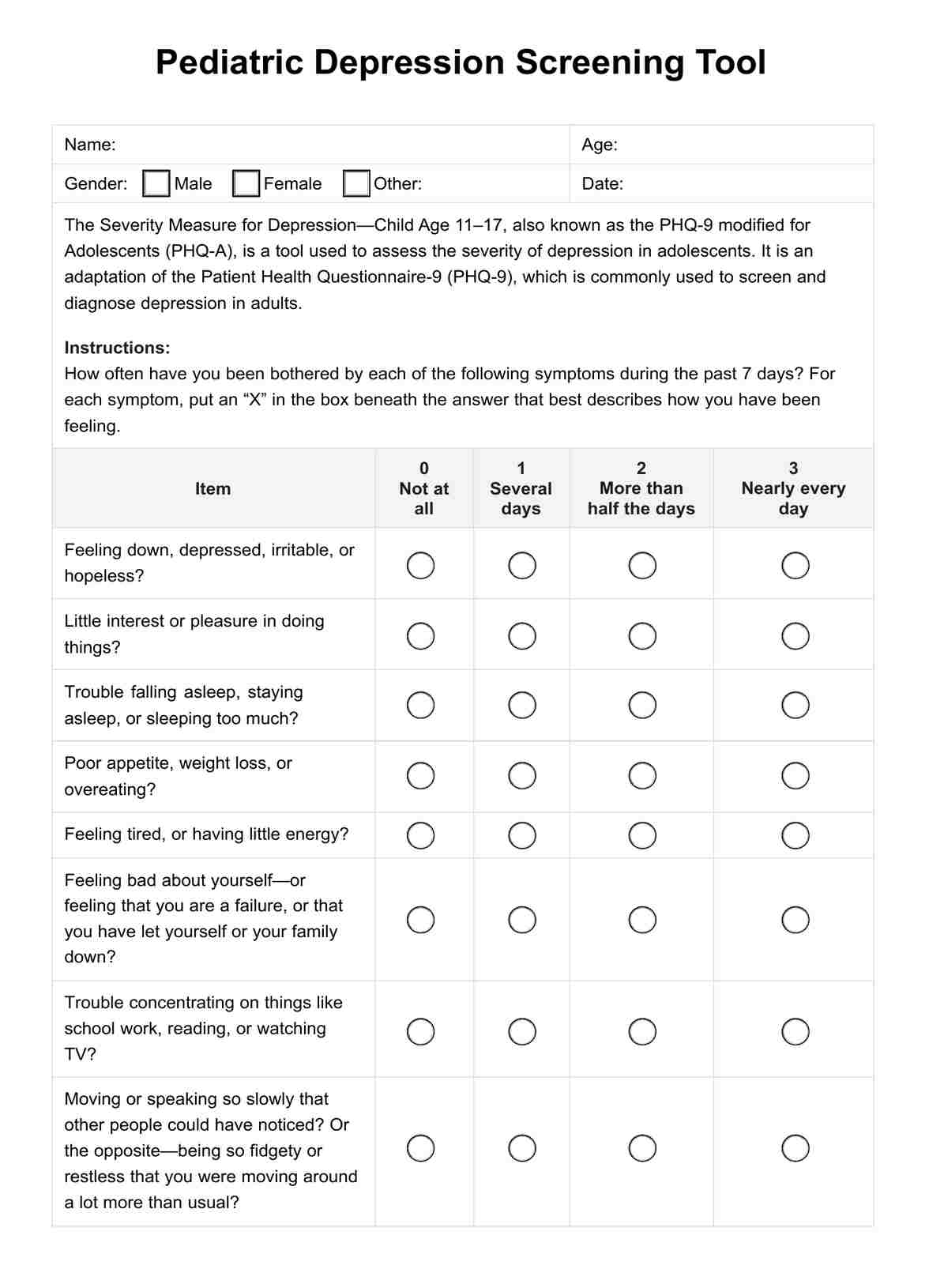
Benefits of using a Pediatric Depression Screening Tool
Screening tools for pediatric depression are essential instruments in the early detection and management of depression in children and adolescents. These tools are pivotal in the mental healthcare continuum, providing numerous benefits for healthcare providers and their young patients.
Early identification and intervention
The primary advantage of using our free Pediatric Depression Screening Tool is the early identification of depressive symptoms, allowing for timely intervention. Early detection is crucial, as it can significantly impact the course and severity of the condition. By identifying depression at its onset, healthcare providers can initiate interventions sooner, which can lead to more effective management of the disorder and a better prognosis for the child or adolescent.
Facilitating timely and appropriate mental health care
Screening tools enable mental health professionals to quickly assess the severity of a child's depressive symptoms and determine the most appropriate course of action. This prompt assessment ensures that children and adolescents receive the mental health care they need without unnecessary delays. Whether the recommended approach involves therapy, medication, or a combination of both, early and accurate screening ensures that each patient's treatment plan is tailored to their needs.
Averting more severe mental health problems
By enabling early detection and treatment, pediatric depression screening tools can help prevent the progression of depression into more severe mental health issues. Untreated depression in childhood and adolescence can lead to a range of negative outcomes, including academic difficulties, substance abuse, and even suicidal ideation. The use of screening tools helps to mitigate these risks by ensuring that young individuals receive the support and treatment they need early in their mental health journey.
Monitoring the effectiveness of ongoing treatment
Another critical benefit of pediatric depression screening tools is their role in monitoring the effectiveness of ongoing treatment plans. These tools provide a standardized method for assessing changes in symptom severity over time, allowing mental health professionals to adjust treatment strategies as needed. Regular screening can help track a patient's progress, promptly identify setbacks, and adapt the treatment plan to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Adjusting strategies as needed
The dynamic nature of mental health treatment for children and adolescents requires a flexible approach capable of adapting to the changing needs of each patient. Pediatric depression screening tools offer valuable insights that can guide these adjustments. By regularly assessing a patient's response to treatment, healthcare providers can make informed decisions about whether to continue, modify, or change the treatment approach, ensuring that it remains aligned with the patient's evolving needs.
Pediatric depression screening tools are indispensable in the early detection, treatment, and management of depression in young individuals. Their use facilitates timely intervention, helps avert more severe mental health issues, and plays a vital role in monitoring treatment effectiveness, thereby contributing to better mental health outcomes for children and adolescents.