It's essential to monitor blood glucose levels frequently, especially during the initial phase of treatment, to assess the effectiveness of insulin therapy and ensure glucose levels are stabilizing. Typically, blood glucose levels should be checked every 1-2 hours until stabilized.
DKA Nursing Care Plan
Create an effective diabetic ketoacidosis nursing care plan with this guide and our PDF template.
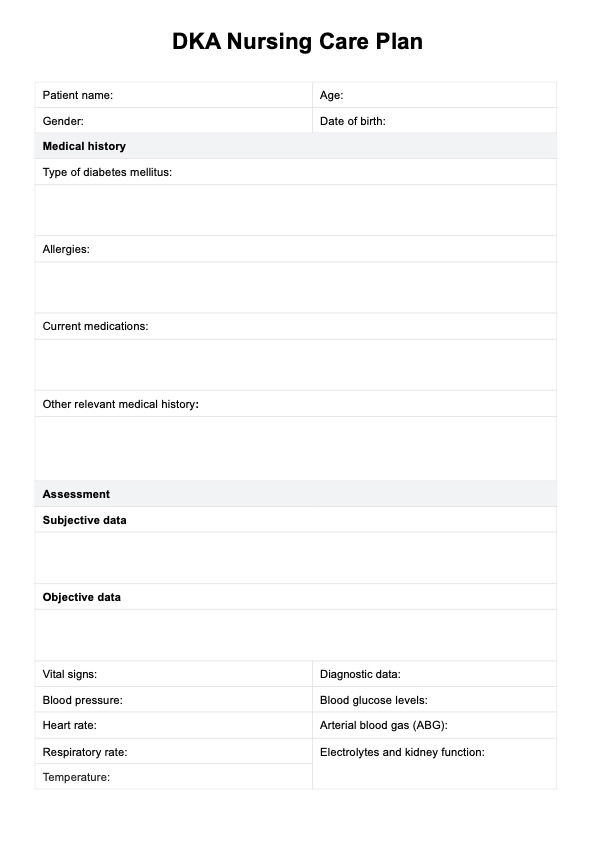
DKA Nursing Care Plan Template
Commonly asked questions
The key steps include administering insulin therapy, administering medications as prescribed, and closely monitoring vital signs such as blood pressure, heart rate, and respiratory rate. This helps assess the patient’s response to treatment and detect any complications early.
Patient education should focus on the importance of monitoring blood glucose levels, administering insulin therapy as prescribed, and recognizing signs of complications. Teaching patients about maintaining hydration and proper medication adherence is also crucial for effective diabetes management.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











