Typically, healthcare providers request a Diabetic Foot Exam Test for patients with diabetes, particularly if they have experienced previous foot complications or exhibit symptoms of neuropathy.
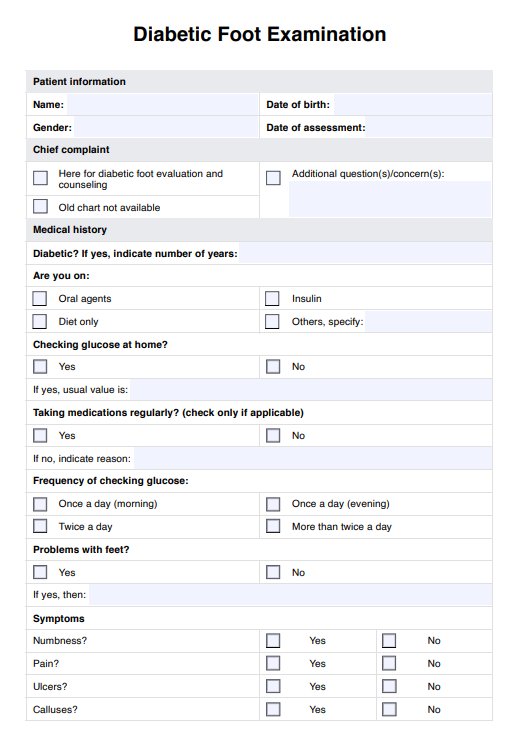
Diabetic Foot Exam
Discover the importance of a Diabetic Foot Exam Test in managing diabetes. Regular foot exams can help prevent complications like ulcers and amputations.
Use Template
Diabetic Foot Exam Template
Commonly asked questions
These tests are usually conducted during routine diabetes management check-ups or more frequently if the patient has a history of foot complications.
These tests are used to identify potential foot complications at an early stage, allowing for timely intervention and prevention of serious complications such as ulcers or amputations.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











