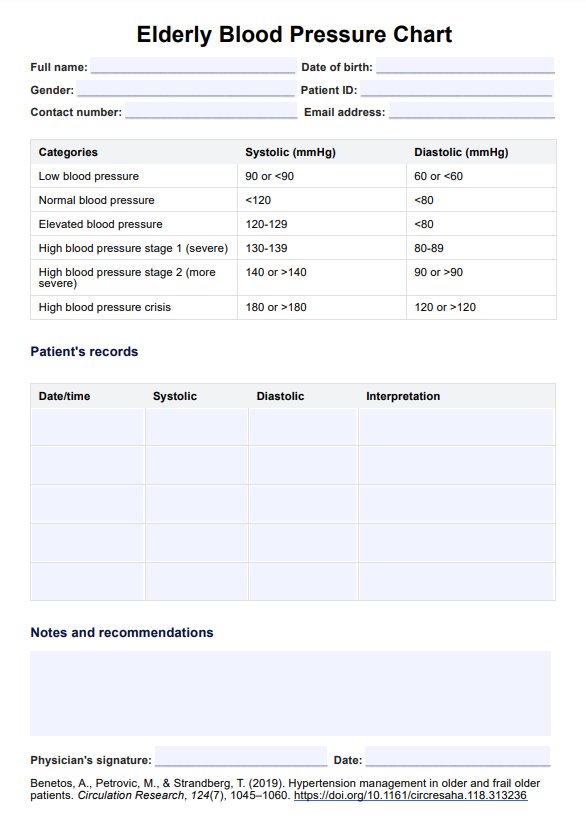
A blood pressure target of less than 130/80 mmHg for adults aged 65 and older. This guideline is based on evidence that lowering blood pressure to this level can reduce the risk of cardiovascular events and mortality in older people.
Elderly Blood Pressure Chart
Get access to a free Elderly Blood Pressure Chart and example. Streamline your practice with this resource from Carepatron.
Elderly Blood Pressure Chart Template
Commonly asked questions
Blood pressure readings above 180/120 mmHg in older adults are considered a hypertensive crisis, which requires immediate medical attention. At these extremely high levels, there is a significant risk of life-threatening complications, such as stroke, heart attack, or organ damage. Prompt treatment is necessary to prevent these serious adverse events.
While high blood pressure is a major concern in older people, excessively low blood pressure (hypotension) can also be problematic. A systolic blood pressure (top number) target of no lower than 120 mmHg for adults 65 and older is recommended. Blood pressure that falls below this level may lead to dizziness, fainting, falls, and other adverse outcomes in the elderly population.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











