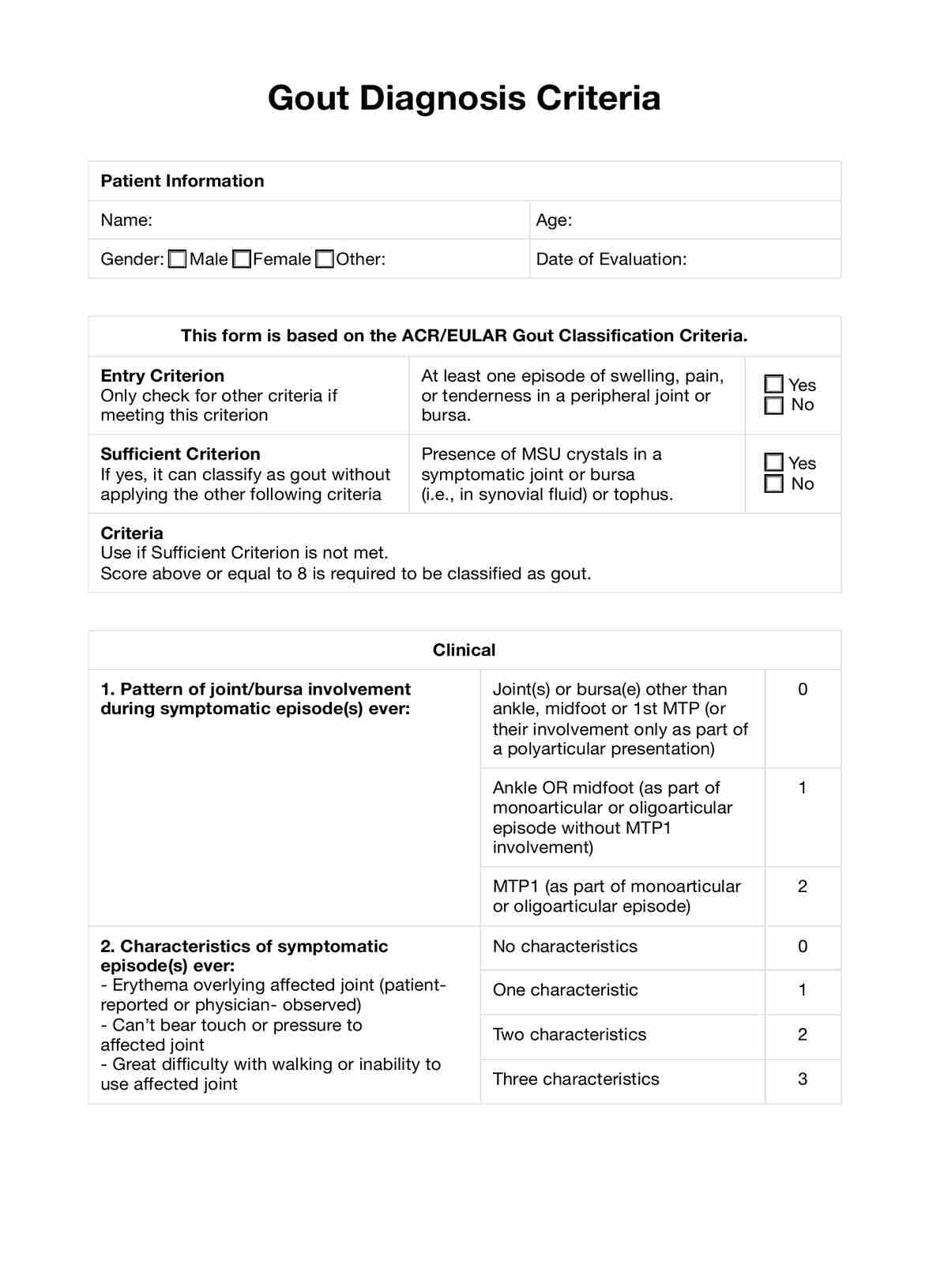
Gout diagnosis is confirmed through a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests (such as serum urate levels), and imaging studies (like ultrasound or X-ray) to detect urate crystals or joint damage.
Gout Diagnosis Criteria
Uncover the essential Gout Diagnosis Criteria here, including symptoms, diagnostic tests, and the American College of Rheumatology guidelines.
Use Template
Gout Diagnosis Criteria Template
Commonly asked questions
The most reliable diagnostic indicator of gout is the presence of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals in the synovial fluid of a symptomatic joint or in a tophus, as observed under a microscope.
The gold standard for diagnosing gout is the identification of monosodium urate crystals in synovial fluid or tophaceous material using polarized light microscopy.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











