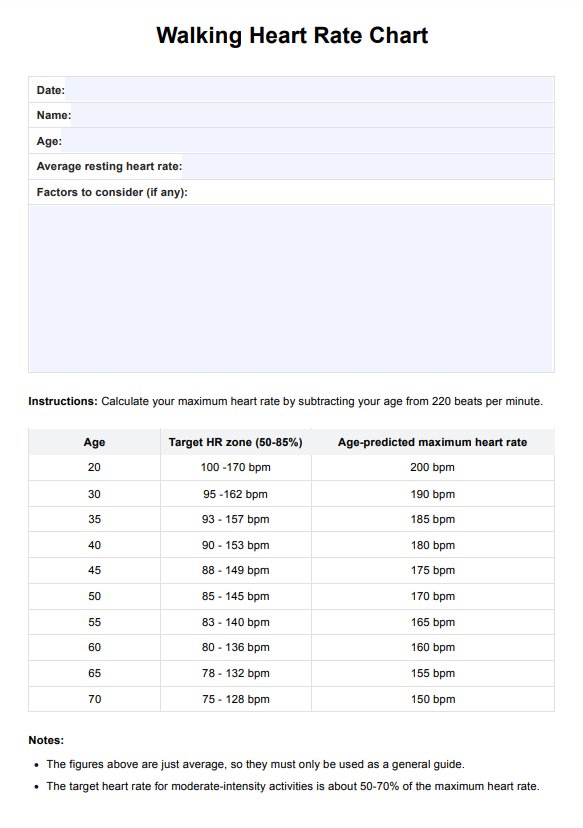
What is a Walking Heart Rate Chart?
A Walking Heart Rate Chart is a tool that physiatrists, sports medicine doctors, etc., can give individuals during brisk walking exercises, optimizing the cardiovascular health benefits of this form of physical activity. When an individual is given a Walking Heart Rate Chart, it can significantly enhance their cardiovascular fitness by ensuring they exercise within the optimal heart rate zones. It is a practical tool for medical practitioners with patients looking to enhance their physical and mental well-being through the benefits of brisk walking, like improved blood flow and better cardiovascular fitness.
In addition, the Walking Heart Rate Chart can be beneficial in various situations. People recovering from sickness or injury who want to move their body without causing extra stress often utilize it, as do those who choose walking as their preferred form of heart-healthy exercise. Furthermore, it helps individuals maintain a pace that challenges the heart and lungs, ensuring they derive maximum benefits from their workout without overexertion.