How does this nursing normal vital signs chart work?
Using the chart helps you monitor vital signs, essential for ensuring patients get the care they need before things get worse. Here's how to use it:
Step 1: Download the template
The template is included in this guide. Click "Use template" to open it on the Carepatron platform, where you can customize it to suit your needs. Alternatively, click "Download" to get a free fillable PDF version of the form.
Step 2: Measure and record the vital signs
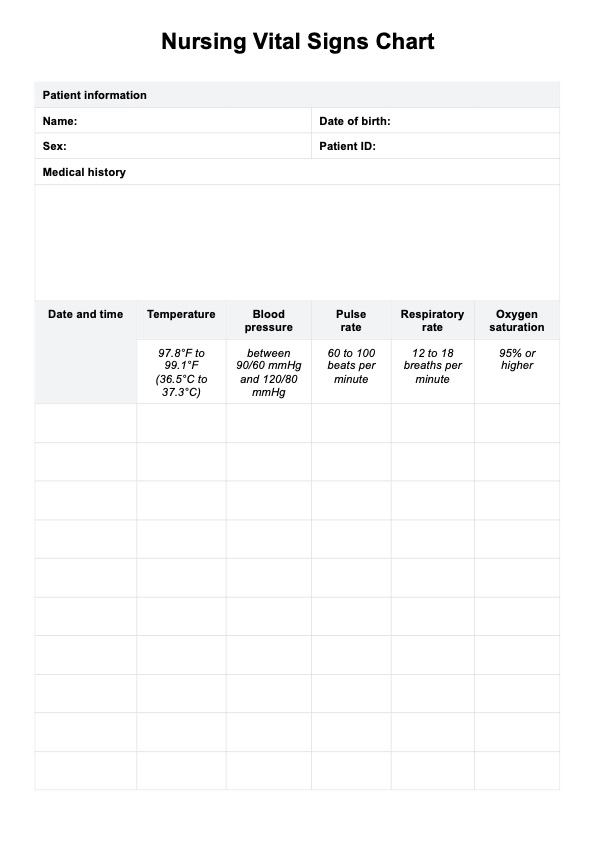
Measure blood pressure, heart rate, temperature, oxygen saturation, and respiratory rate. Record each of these values in the corresponding sections on the chart.
Step 3: Compare with normal vital sign ranges
After entering the values, compare them to the normal ranges for vital signs. This helps identify any abnormal readings that might require further attention or action. Here are the values for each vital sign (Minnesota Department of Health, 2022; Mount Sinai Health System, 2023):
- Normal body temperature: 97.8°F to 99.1°F (36.5°C to 37.3°C)
- Blood pressure: Between 90/60 mmHg and 120/80 mmHg
- Pulse rate: 60 to 100 beats per minute
- Normal respiratory rate: 12 to 18 breaths per minute
- Oxygen saturation: 95% or higher
It is worth noting that normal vital signs change depending on factors like age, sex, weight, fitness level, and general health. When it comes to pediatric vital signs, they vary from those of adults, so it's essential to follow age-specific guidelines to assess their health properly.
Step 4: Update regularly and track trends
Continue recording the patient's vital signs at regular intervals, updating the chart each time. Our chart has a date and time stamp column, which will help you track trends over time and quickly notice any changes in the patient's condition.
Step 5: Share and communicate with the healthcare team
Ensure you share the updated vital signs chart with the healthcare team to provide a clear patient status overview. Effective communication will help them make informed decisions about their care.