What is a Heart Calcium Score Chart?
A Heart Calcium Score Chart is derived from a Coronary Artery Calcium (CAC) test, a specialized heart CT scan. The coronary calcium scan utilizes multidetector CT (MDCT) technology that captures detailed images of the coronary arteries to identify and measure calcium deposits or blood flow (American Heart Association, Inc., 2023).
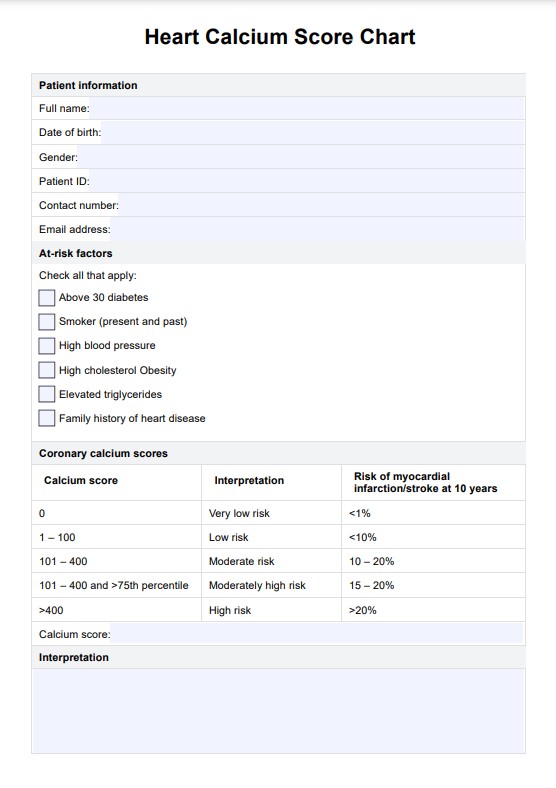
The CAC test provides a “calcium score,” indicating the quantity of calcium in the coronary arteries. This coronary artery calcium scoring reflects the level of plaque present, which can predict future heart disease risk, including heart attacks. High calcium scores correlate with a higher likelihood of significant coronary artery disease.
The results of the calcium score test is especially beneficial for patients at intermediate risk of heart disease. They assist healthcare professionals in making informed decisions regarding initiating preventive therapies such as statins or low-dose aspirin. It is particularly useful for individuals uncertain about starting or restarting statin therapy or those with intermediate risk factors.
However, it is important to note that CAC testing is not typically recommended for routine screening in low-risk individuals without symptoms, and it involves a radiation dose comparable to that of a mammogram (American Heart Association, Inc., 2023).
A Heart Calcium Score Chart is a valuable tool used to interpret and understand the results of a CAC test. This can help healthcare professionals assess an individual's risk of developing heart disease and determine a suitable treatment plan.