Everybody gets stressed. People get stressed because of work, responsibilities, shocking news, traumatic events, catastrophes, personal problems, sickness like cardiovascular disease, and more. Every person will evaluate their own stress differently, and so too will their reaction to and coping mechanisms. Read on to learn about the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS), a tool about evaluating a person's perceived stress that can help you understand the level of experienced stress your patients have, how they view their stress, and how their views on their stress influence how they respond to it.
## **How can you measure perceived stress?**
Perceived stress involves the feelings or thoughts an individual experiences in response to the demands or pressures of a situation, known as stressors (Cohen et al., 1983). In a nutshell, perceived stress reflects how an individual evaluates and copes with the stressors in their life.
Perceived stress can vary widely from person to person, even in response to the same stressor. For example, some individuals may perceive a demanding work deadline as highly stressful, while others may view it as a challenge and an opportunity for growth.
Measuring perceived stress is crucial for understanding an individual's subjective experience of stress and its potential impact on their health and well-being. One of the most widely used and validated tools for assessing perceived stress is the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS), developed by Cohen and colleagues (1983).
## **What is the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS?)**
The PSS is a self-reported questionnaire that assesses an individual's stress perception levels over the past month. It is a global measure of stress, meaning it does not focus on specific sources of stress but rather on the degree to which life situations are appraised as stressful (Lee, 2012).
The PSS is available in three versions: the original 14-item scale (PSS-14), a 10-item version (PSS-10), and a 4-item version (PSS-4). The most commonly used is the PSS-10, which consists of six negative items and four positive items and was developed using factor analysis-based data.
The PSS-10 has been widely studied by scientific and research publications and validated across various populations and community samples. Factor analysis studies have generally supported a one-factor or two-factor structure, with the two factors representing perceived helplessness and perceived self-efficacy (Cohen & Williamson, 1988; Roberti et al., 2006).
### **Psychometric properties**
The PSS boasts strong psychometric properties, making it a reliable and valid tool for assessing stress in a probability sample, including pregnant and postpartum women, college students, and cardiac patients.
The PSS-10 has normative data based on various populations. It has shown good internal consistency reliability, with Cronbach's alpha ranging from 0.75 to 0.86 in different studies (Cohen, 1988; Roberti et al., 2006; Wongpakaran & Wongpakaran, 2010). Test-retest reliability over two days to two weeks has also been reported as adequate, with correlations ranging from 0.55 to 0.85 (Cohen et al., 1983; Roberti et al., 2006).
The PSS has also demonstrated good construct validity, with higher scores being associated with higher levels of depression, anxiety, and risk of contracting an infectious disease.
Additionally, the PSS has great concurrent validity and has been positively correlated with other measures of stress, such as the [Beck Depression Inventory (BDI)](https://www.carepatron.com/templates/beck-depression-inventory), the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale, the [Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale](https://www.carepatron.com/templates/beck-depression-inventory), and the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI), and the Thai Depression Inventory (Wongpakaran & Wongpakaran, 2010; Andreou et al., 2011; Baik et al., 2019). It was also used alongside measures for assessing anxiety and depression in adults and university student populations (Lee, 2012), as well as (early) adolescents (Sood et al., 2013), making it a great tool to add to comprehensive assessment of people with other mental health issues.
This was further supplemented by the correlation with the [Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale](https://www.carepatron.com/templates/center-for-epidemiologic-studies-depression-scale-ces-d), which had statistically significant correlation coefficients with the PSS (Cristóbal-Narváez et al., 2021).
Confirmatory factor analysis studies have generally supported the one-factor structure or the two-factor model of the PSS-10, providing evidence for its construct validity (Roberti et al., 2006; Wongpakaran & Wongpakaran, 2010).
While the Cohen Perceived Stress Scale is a valuable tool, it should not be used as a diagnostic instrument on its own. It's important to consider other measures alongside it for a comprehensive psychometric evaluation and data analysis. Here are some additional options to tap into the different aspects of emotional and psychological stress:
- **Depression Anxiety Stress Scale (DASS-21)**: This is a 21-item scale measuring depression, anxiety, and stress severity.
- **General Health Questionnaire (GHQ-12)**: This is a 12-item scale assessing mental health status in the general population.
- **Beck Depression Inventory (BDI-II)**: This is a 21-item scale specifically designed to measure the severity of depression.
## **How do you use this Perceived Stress Scale (PSS)?**
Using the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS) can provide valuable insights into an individual's subjective experience of stress. We recommend using this tool because it's a great way to understand their perceptions of their stress. The information can help you determine what other aspects of a patient's mental health you should examine, including other factors such as the environments they commonly find themselves in. Our template is also easy to use; there's nothing overly complicated you need to be familiar with to use it.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to administer and interpret the PSS:
### **Step 1: Administer the PSS**
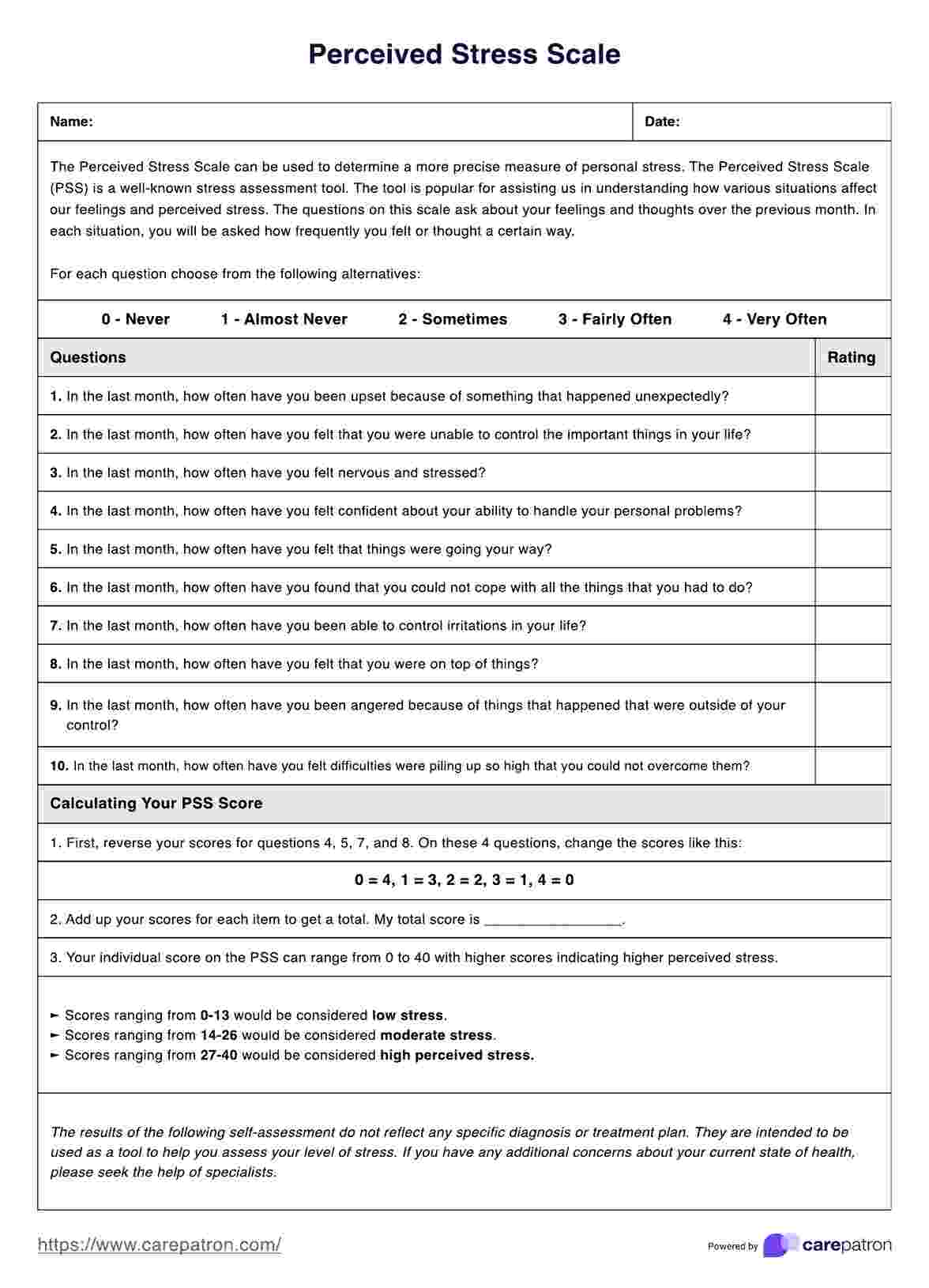
The PSS consists of 10 items that assess an individual's perception of stress over the past month. Participants rate each item on a scale from 0 (never) to 4 (very often). The questionnaire can be self-administered or administered verbally.
Sample items include:
- In the last month, how often have you been upset because of something that happened unexpectedly?
- In the last month, how often have you felt that you were unable to control the important things in your life?
- In the last month, how often have you felt nervous and stressed?
The only thing you or your patient has to do is to indicate the number rating they believe corresponds to them based on the item being answered.
### **Step 2: Calculate the PSS score**
First, reverse the scores for the positively stated items (items 4, 5, 7, and 8) to calculate the PSS score. Then, sum up the scores for all 10 items. Higher scores indicate higher levels of perceived stress.
### **Step 3: Interpret the PSS score**
Scores ranging from 0 to 13 would be considered low stress. Scores ranging from 14 to 26 would be considered moderate stress. Scores ranging from 27 to 40 would be considered high perceived stress.
### **Step 4: Consider individual factors**
When interpreting the PSS score, it's essential to consider individual factors such as age, gender, and cultural background. Additionally, the PSS should be used with other assessments and clinical information to understand the individual's stress experience and coping strategies comprehensively.
### **Step 5: Use in treatment planning and monitoring**
The PSS can be useful for healthcare practitioners to identify individuals who may benefit from stress management interventions. It can also be administered periodically to monitor changes in perceived stress levels due to treatment or life circumstances.
## **Scoring and interpretation**
Accurately interpreting the results of the Perceived Stress Scale is crucial for understanding an individual's subjective experience of stress and developing appropriate coping strategies.
To score the PSS, first, reverse the scores for the positively stated items (items 4, 5, 7, and 8). For example, if a participant scores a 4 on item 4, it should be coded as 0. Then, sum up the scores for all 10 items to get the total PSS score.
The total PSS score can range from 0 to 40, with higher scores indicating higher levels of perceived stress. Scores ranging from 0 to 13 are considered low stress, 14 to 26 are regarded as moderate stress, and 27 to 40 are considered high perceived stress.
Additionally, the PSS should be used with other assessments and clinical information to comprehensively understand the individual's stress experience and coping strategies. It's not recommended to rely solely on the PSS score for diagnostic or treatment purposes.
## **Common coping strategies for stress**
One way of helping your patients/clients deal with stress is to come up with stress management plans. Here are some coping strategies to include in your plans:
- **Encourage your patients to get regular exercise**. Exercise is proven to increase the body's production of endorphins, which are neurotransmitters that help make us feel happy. This helps with mood regulation. Exercise also helps provide relief when dealing with stressors (Mayo Clinic Staff, 2025).
- **Tell your patients to avoid caffeine when stressed**. It's normal for people to drink coffee or eat when stressed as a way to cope or calm down, but caffeine can help stimulate anxiety in people. Stress can make people feel anxious, and caffeine won't help. It's also not great for people who have hypertension because caffeine can raise a person's blood pressure, and both stress and caffeine can prolong the level of raised blood pressure (Hartley et al., 2001).
- **It's important to have hobbies**. Everyone needs a distraction from stress, so having hobbies is essential to helping people calm down when dealing with stress. Having rest breaks or setting aside time after a busy day at school or work to indulge hobbies is helpful when it comes to relaxing after a period of stress.
- **If your patient can afford it, have them take a vacation away from home**. Stress triggers are likely in the environments that patients frequent (e.g., home, school, work). By going on vacation away from home, people will be placed in a different environment without any of their stressors. This will help them relax and recharge, especially if they've been feeling tired. It could even clear their minds. Do recommend nature escapes or rural areas. Of course, other environments can have their own set of things that could stress out people, but a change of scenery is always nice.
- **Encourage your patient to eat well and sleep well**. It's important that people get enough sleep and eat enough food. Not being well-rested and not being well-fed could affect how people cope with stress. Coping with stress requires energy and a clear mind.
## **References**
Andreou, E., Alexopoulos, E. C., Lionis, C., Varvogli, L., Gnardellis, C., Chrousos, G. P., & Darviri, C. (2011). Perceived Stress Scale: reliability and validity study in Greece. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 8(8), 3287–3298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph8083287
Baik, S. H., Fox, R. S., Mills, S. D., Roesch, S. C., Sadler, G. R., Klonoff, E. A., & Malcarne, V. L. (2019). Reliability and validity of the Perceived Stress Scale-10 in Hispanic Americans with English or Spanish language preference. Journal of Health Psychology, 24(5), 628–639. https://doi.org/10.1177/1359105316684938
Cohen, S., Kamarck, T., & Mermelstein, R. (1983). A global measure of perceived stress. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 24(4), 385–396. https://doi.org/10.2307/2136404
Cohen, S. (1988). Perceived stress in a probability sample of the United States. In S. Spacapan & S. Oskamp (Eds.), The social psychology of health (pp. 31–67). Sage Publications, Inc.
Cohen, S., & Janicki-Deverts, D. (2012). Who's stressed? Distributions of psychological stress in the United States in probability samples from 1983, 2006, and 2009. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 42(6), 1320–1334. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1559-1816.2012.00900.x
Cristóbal-Narváez, P., Haro, J. M., & Koyanagi, A. (2021). Longitudinal association between perceived stress and depression among community-dwelling older adults: Findings from the Irish Longitudinal Study on Ageing. Journal of Affective Disorders, 299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2021.12.041
Hartley, T. R., Lovallo, W. R., Whitsett, T. L., Sung, B. H., & Wilson, M. F. (2001). Caffeine and Stress: Implications for Risk, Assessment, and Management of Hypertension. The Journal of Clinical Hypertension, 3(6), 354–382. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-6175.2001.00478.x
Lee, E. H. (2012). Review of the psychometric evidence of the Perceived Stress Scale. Asian Nursing Research, 6(4), 121–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anr.2012.08.00
Mayo Clinic Staff. (2025, March 26). Exercise and stress: Get moving to manage stress. Mayo Clinic; Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/stress-management/in-depth/exercise-and-stress/art-20044469
Roberti, J. W., Harrington, L. N., & Storch, E. A. (2006). Further psychometric support for the 10-item version of the Perceived Stress Scale. Journal of College Counseling, 9(2), 135–147. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2161-1882.2006.tb00100.x
Sood, S., Bakhshi, A., & Devi, P. (2013). An assessment of perceived stress, resilience and mental health of adolescents living in border areas. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, 3(1), 1-4.
Wongpakaran, N., & Wongpakaran, T. (2010). The Thai version of the PSS-10: An investigation of its psychometric properties. Biopsychosocial Medicine, 4, 6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1751-0759-4-6