A safe bilirubin level for adults is generally below 1.5 mg/dL. Bilirubin levels above this threshold can indicate liver dysfunction or other underlying medical conditions. In adults, bilirubin levels above 2.5 mg/dL may be considered toxic and can lead to complications such as jaundice, liver damage, and even liver failure.
Bilirubin Levels
Monitor, assess, and manage bilirubin levels effectively through Bilirubin Levels Charts. Discover more about this life-saving tool.
Bilirubin Levels Template
Commonly asked questions
A toxic level of bilirubin in adults is typically considered to be above 3.5 mg/dL. At this level, bilirubin can accumulate in the brain and other organs, leading to severe complications such as kernicterus, a condition characterized by brain damage and intellectual disability. Bilirubin levels above 5 mg/dL are often considered life-threatening and require immediate medical attention.
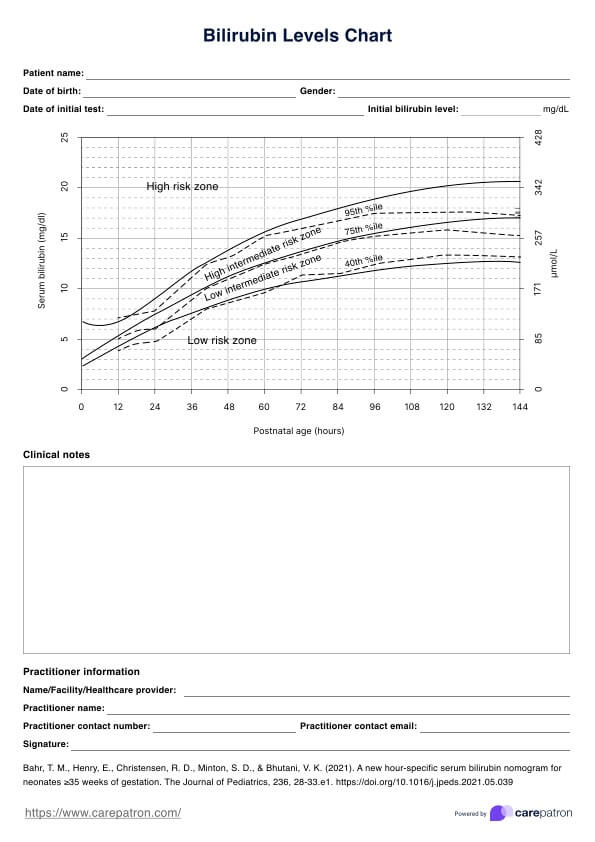
A Bilirubin Levels in Newborns Chart would consider below 12 mg/dL as an acceptable bilirubin level among newborns. Newborns have increased bilirubin production compared to adults due to the breakdown of fetal hemoglobin, which is rich in bilirubin. Bilirubin levels above 15 mg/dL in newborns can indicate jaundice, which is a common condition in newborns. In severe cases, bilirubin levels above 20 mg/dL may require phototherapy or exchange transfusion to prevent complications.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











