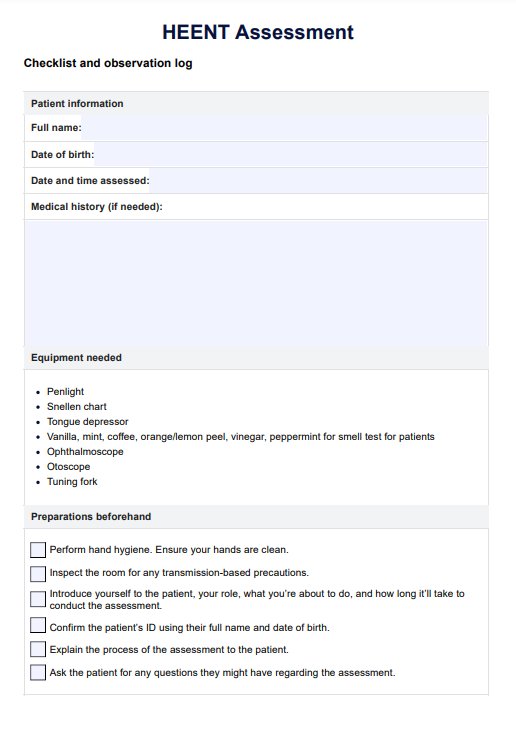
How to conduct the HEENT Assessment?
If we're being honest, the HEENT examination is a lot! If you're reading this and you conduct this assessment occasionally, use it as a refresher on what you need to do.
Step 1: Prepare your tools and resources
Aside from having a copy of the HEENT examination template, it's also best to have all the tools in a clinician's toolbox, like a tongue depressor, otoscope, small flashlight for the eyes, etc. Then, ensure that you have easy access to a place to wash your hands during the assessment because you will be touching the patient's head multiple times.
Step 2: Examine the head
Assess a patient's skull, scalp, and face How to conduct the HEENT Assessment?
If we're being honest, the HEENT examination is a lot! If you're reading this and you conduct this assessment occasionally, use it or our HEENT assessment example template as a refresher on what you need to do.
Step 1: Prepare your tools and resources
Aside from having a copy of the HEENT examination template, it's also best to have all the tools in a clinician's toolbox, like a tongue depressor, otoscope, small flashlight for the eyes, etc. Then, ensure that you have easy access to a place to wash your hands during the assessment because you will be touching the patient's head multiple times.
Step 2: Examine the head
Assess a patient's skull, scalp, and face and gauge them for any abnormalities:
- Visually inspect the head and face for symmetry or asymmetry.
- Visually inspect the hair for color, distribution, and texture.
- Palpate the scalp and skull for tenderness, flaking, lesions, parasites, lumps, swelling, and deformities.
Step 3: Examine the eyes
Next, examine the patient's eyes:
- Check the alignment of the eyes.
- Check for the presence of discharge, irritation, and redness.
- Check the eyelids for any drooping.
- Check the strength of each eyelid by having your patient shut their eyes and try to open them. If the eyelids are strong, you shouldn't be able to.
- Check the sclera and conjunctiva for both eyes.
- Check the cornea, iris, and lens for transparency.
- Check the pupils and compare them. Test them by conducting the PERRLA Eye Exam.
- Check the six cardinal positions of the gaze.
- Check for conjugate gaze.
- Check for nystagmus.
- Check the visual fields in both eyes: medially/laterally, superiorly/inferiorly.
- Check their visual acuity using a Snellen Chart.
- Check their ocular fundi using an ophthalmoscope.
- Check the transparency of the anterior and posterior chambers.
- Check the red reflex of the retina.
Step 4: Examine the ears
After this, move on to the patient's ears:
- Do an external inspection of the pinna for abnormalities that may point to skin cancer and gout, as well as the external auditory canal for redness, swelling, and earwax.
- Check the auricle, canal, and ear drum for any changes in color, symmetry, elasticity and presence of tenderness or lesions.
- Check the tympanic membrane for any changes in color, shape, transparency, integrity, and the presence of bulging or scarring.
- If there is earwax, clear the ears.
- Check the middle ear canal.
- Conduct the Whisper Test as part of the gross hearing test to check for hearing acuity.
- If their acuity doesn't seem good, conduct the Weber and Rinne tests to check for deafness. These require a vibrating tuning fork.
Step 5: Examine the nose and lymph nodes
Then, inspect the nose's color, shape, size, and symmetry:
- Visually inspect the nose for any presence of drainage, tenderness, and masses.
- Use an otoscope or nasal speculum to inspect the nasal passages for patency, nasal mucosa for color, nasal septum for deviation, and turbinates for color and swelling.
- Check the frontal and maxillary sinuses for tenderness and infections. Ensure that they are not tender to palpation.
- Check their sense of smell or conduct the CN I test (Olfactory nerve) by having them sniff an orange or lemon peel, coffee, vinegar, vanilla, or peppermint.
- Check if the patient reports difficulty smelling.
Step 6: Do an oral and throat examination
Then, an oral and throat exam will follow:
- Inspect the lips for color, moisture, masses, cracks, sores, fissures, and symmetry.
- Inspect the oral mucosa for color, lesions, dryness, moisture, masses, and swelling.
- Inspect the tongue for color, thickness, moisture, symmetry of movement left and right, and deviations from the midline. Also, check the mouth, tongue, and floor for masses and swelling.
- Conduct an oral examination to inspect the posterior pharynx.
- Inspect the teeth for their general condition and evaluate if any teeth are missing.
- Check for any oral cavity. Examine the hard and soft palate for integrity and length.
- Inspect the gums for color, texture, swelling, retraction, and bleeding. Check for signs of periodontal disease.
- Inspect the uvula for movement, position, size, symmetry, and color.
- Pharynx inspection for color, redness, inflammation, exudate, masses, and lesions.
- Inspect the tonsils for size, color, inflammation, and exudate.
- Inspect the salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary) for patency and signs of inflammation or redness.
- Check the patient's gag reflex and ability to swallow.
- Check for an enlarged thyroid gland at the suprasternal notch.
Step 7: Assess the neck
This physical assessment has six components. The last one is the Neck. It should have been called HEENT and Neck Exam if you ask us. Without further ado, here are the things you need to check for the Neck:
- Check neck muscles for symmetry, masses, and swelling.
- Palpate the cervical lymph nodes for any swelling or tenderness.
- Assess the head and the neck's range of motion.
- Assess the strength of the trapezius muscle and cervical muscle.
- Check the trachea for deviation.
- Check the thyroid gland for enlargement, any nodules, and masses.
- Check the posterior aspect of the neck for tenderness in the cervical point.
Step 8: Record findings
If there are any abnormal findings, it would be best to document them and update the patient's health history to record any risk factors and other problems that have been detected.
gauge them for any abnormalities:
- Visually inspect the head and face for symmetry or asymmetry.
- Visually inspect the hair for color, distribution, and texture.
- Palpate the scalp and skull for tenderness, flaking, lesions, parasites, lumps, swelling, and deformities.
Step 3: Examine the eyes
Next, examine the patient's eyes:
- Check the alignment of the eyes.
- Check for the presence of discharge, irritation, and redness.
- Check the eyelids for any drooping.
- Check the strength of each eyelid by having your patient shut their eyes and try to open them. If the eyelids are strong, you shouldn't be able to.
- Check the sclera and conjunctiva for both eyes.
- Check the cornea, iris, and lens for transparency.
- Check the pupils and compare them. Test them by conducting the PERRLA Eye Exam.
- Check the six cardinal positions of the gaze.
- Check for conjugate gaze.
- Check for nystagmus.
- Check the visual fields in both eyes: medially/laterally, superiorly/inferiorly.
- Check their visual acuity using a Snellen Chart.
- Check their ocular fundi using an ophthalmoscope.
- Check the transparency of the anterior and posterior chambers.
- Check the red reflex of the retina.
Step 4: Examine the ears
After this, move on to the patient's ears:
- Do an external inspection of the pinna for abnormalities that may point to skin cancer and gout, as well as the external auditory canal for redness, swelling, and earwax.
- If there is earwax, clear the ears.
- Check the middle ear canal.
- Perform an Otoscopy with an otoscope: check the color and shape of the eardrums (and if they're bulging or retracted), cone of light, umbo, the long and short processes of the malleus, pars tensa, pars flaccida, and the annulus.
- Conduct the Whisper Test as part of the gross hearing test to check for hearing acuity.
- If their acuity doesn't seem good, conduct the Weber and Rinne tests to check for deafness. These require a vibrating tuning fork.
Step 5: Examine the nose and lymph nodes
Then, inspect the nose's color, shape, size, and symmetry:
- Visually inspect the nose for any presence of drainage, tenderness, and masses.
- Use an otoscope or nasal speculum to inspect the nasal passages for patency, nasal mucosa for color, nasal septum for deviation, and turbinates for color and swelling.
- Check the frontal and maxillary sinuses for tenderness and infections.
- Check the frontal and maxillary sinuses are not tender to palpitation.
- Check their sense of smell or conduct the CN I test (Olfactory nerve) by having them sniff an orange or lemon peel, coffee, vinegar, vanilla, or peppermint.
- Check if the patient reports difficulty smelling.
Step 6: Do an oral and throat examination
Then, a oral and throat exam will follow:
- Inspect the lips for color, moisture, masses, cracks, sores, fissures, and symmetry.
- Inspect the oral mucosa for color, lesions, dryness, moisture, masses, and swelling.
- Inspect the tongue for color, thickness, moisture, symmetry of movement left and right, and deviations from the midline. Also, check the mouth, tongue, and floor for masses and swelling.
- Conduct an oral examination to inspect the posterior pharynx.
- Inspect the teeth for their general condition and evaluate if any teeth are missing.
- Check for any oral cavity. Examine the hard and soft palate for integrity and length.
- Inspect the gums for color, texture, swelling, retraction, and bleeding. Check for signs of periodontal disease.
- Inspect the uvula for movement, position, size, symmetry, and color.
- Pharynx inspection for color, redness, inflammation, exudate, masses, and lesions.
- Inspect the tonsils for size, color, inflammation, and exudate.
- Inspect the salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary) for patency and signs of inflammation or redness.
- Check the patient's gag reflex and ability to swallow.
- Check for an enlarged thyroid gland at the suprasternal notch.
Step 7: Assess the neck
This physical assessment has six components. The last one is the Neck. It should have been called HEENT and Neck Exam if you ask us. Without further ado, here are the things you need to check for the Neck:
- Check neck muscles for symmetry, masses, and swelling.
- Palpate the cervical lymph nodes for any swelling or tenderness.
- Assess the head and the neck's range of motion.
- Assess the strength of the trapezius muscle.
- Assess the strength of the cervical muscle.
- Check the trachea for deviation.
- Check the thyroid gland for enlargement.
- Check the thyroid gland for any nodules and masses.
- Check the posterior aspect of the neck for tenderness in the cervical point.
Step 8: Record findings
If there are any abnormal findings, it would be best to document them and update the patient's health history to record any risk factors and other problems that have been detected.