Nursing interventions for atrial fibrillation include several key actions: administering prescribed medications like beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, or anticoagulants based on the patient's condition; regularly monitoring vital signs such as blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation to assess treatment response and detect complications; and conducting a thorough assessment of symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, and fatigue to evaluate the condition's severity and ensure appropriate care.
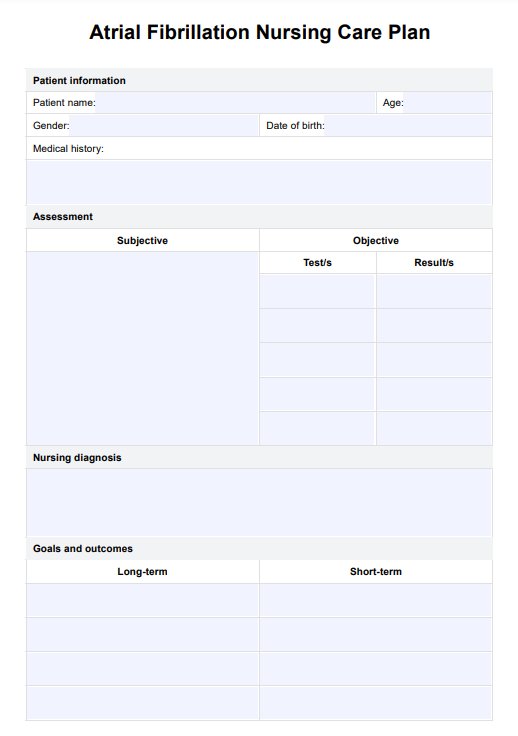
Atrial Fibrillation Nursing Care Plan
Streamline patient care with our Atrial Fibrillation Nursing Care Plan Template - a comprehensive guide for effective management and treatment.
Atrial Fibrillation Nursing Care Plan Template
Commonly asked questions
The SMART goal for atrial fibrillation management is to maintain a normal heart rate, prevent future episodes, reduce the risk of stroke and other complications, and enhance overall quality of life. This can be achieved through lifestyle changes like a healthy diet, regular physical activity, stress management, and quitting smoking.
Some key areas that nurses should monitor include the patient's heart rate and rhythm, blood pressure, oxygen saturation levels, and any potential signs of complications such as chest pain or shortness of breath.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











