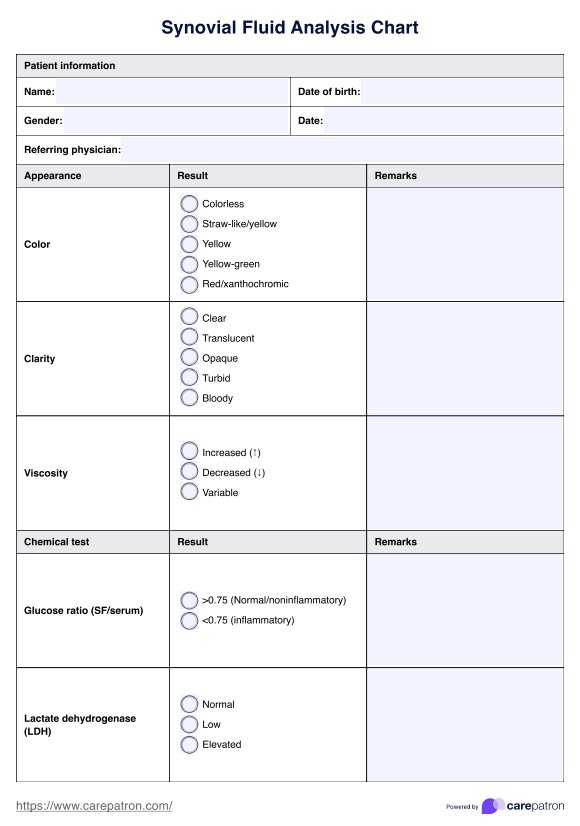
Synovial fluid analysis, or joint fluid analysis, is a diagnostic test that examines the synovial fluid—the lubricating liquid in joints—to assess joint health. This test evaluates the fluid's chemical composition, white blood cell count, and the presence of crystals or bacteria. It is performed to diagnose conditions such as gout, septic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and other joint disorders. Identifying the cause of joint pain, swelling, or effusion helps guide appropriate treatment.
Synovial Fluid Analysis
Discover a free Synovial Fluid Analysis Chart PDF. Download this template to streamline your patient's test records.
Synovial Fluid Analysis Template
Commonly asked questions
Joint aspiration, or arthrocentesis, is a procedure where a needle is inserted into an affected joint to remove excess fluid. This fluid is then analyzed in a synovial fluid analysis. Joint aspiration is commonly performed when joint effusion, or the accumulation of fluid in the joint space, causes swelling and discomfort. The procedure not only relieves pressure in the joint but also provides a sample for diagnostic testing.
Synovial fluid analysis can identify a range of joint conditions, including bacterial arthritis, gout, pseudogout, and rheumatic diseases. Abnormal synovial fluid, such as cloudy or discolored fluid, may indicate infection or inflammation. Elevated white blood cell counts suggest septic or inflammatory arthritis, while the presence of uric acid or calcium pyrophosphate crystals confirms gout or pseudogout. These findings help distinguish between inflammatory and non-inflammatory joint disorders.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











