Primary care physicians, rheumatologists, and other specialists may request an ESR test to help diagnose inflammation-related conditions.
Sedimentation Rate Levels Chart
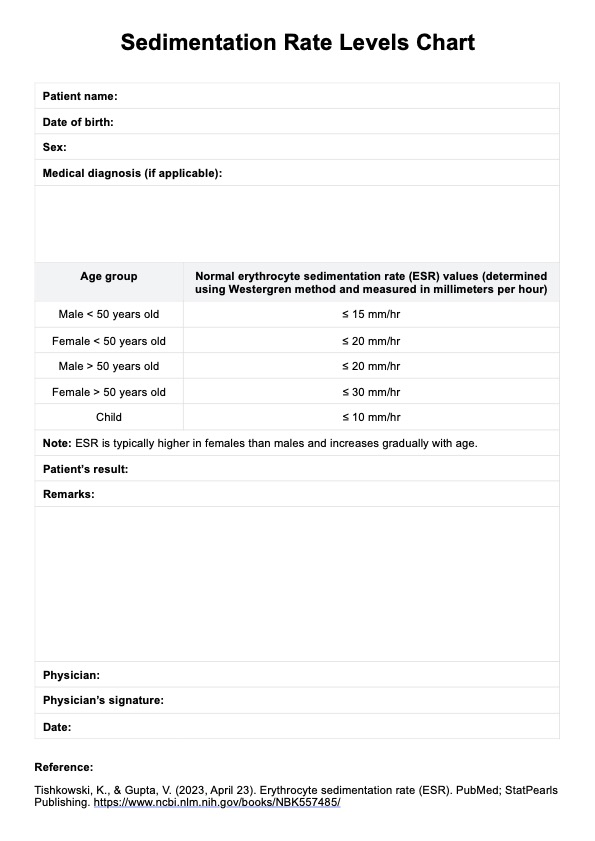
Download a free Sedimentation Rate Levels Chart to track ESR test results for inflammation indicators and manage patient care effectively.
Use Template
Sedimentation Rate Levels Chart Template
Commonly asked questions
Sedimentation Rate Levels Charts are used when symptoms suggest conditions like arthritis, vasculitis, or inflammatory bowel disease and to monitor the activity of these conditions.
Sedimentation Rate Levels Charts are used to record and compare ESR results with normal ranges to assess the presence and severity of inflammation.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











