Lab Values Charts are used during routine check-ups, in the management of chronic diseases, and acute care settings.
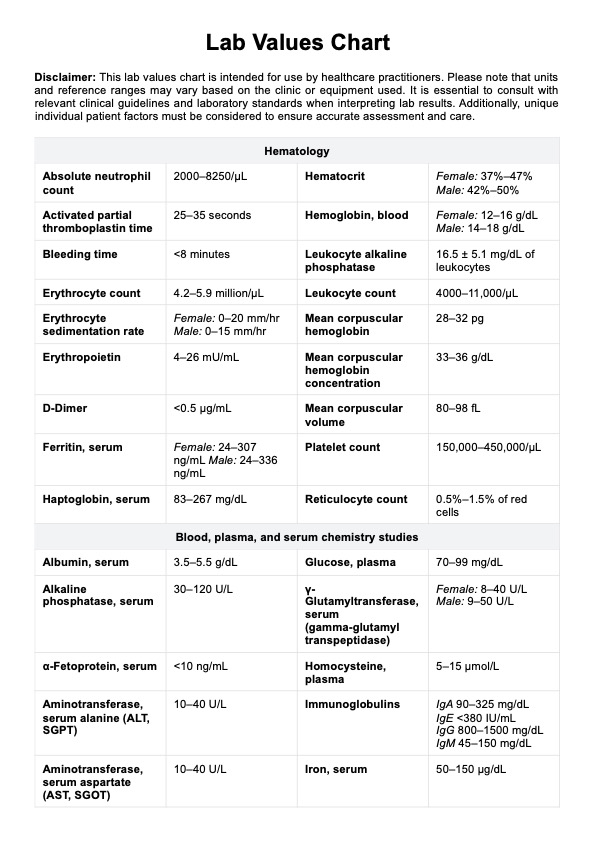
Lab Values Chart
Quickly reference the normal ranges with our Lab Values Chart, your tool for accurate and efficient clinical diagnostics and patient care.
Use Template
Lab Values Chart Template
Commonly asked questions
To read lab blood test results, one should familiarize themselves with the reference ranges provided for each test, understand the significance of each component (like WBC, RBC, hemoglobin), and consider the context of the patient's overall health, as results can vary based on individual factors.
Lab Value Charts compare patient lab results with normal ranges to assist in diagnosis and treatment planning.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











