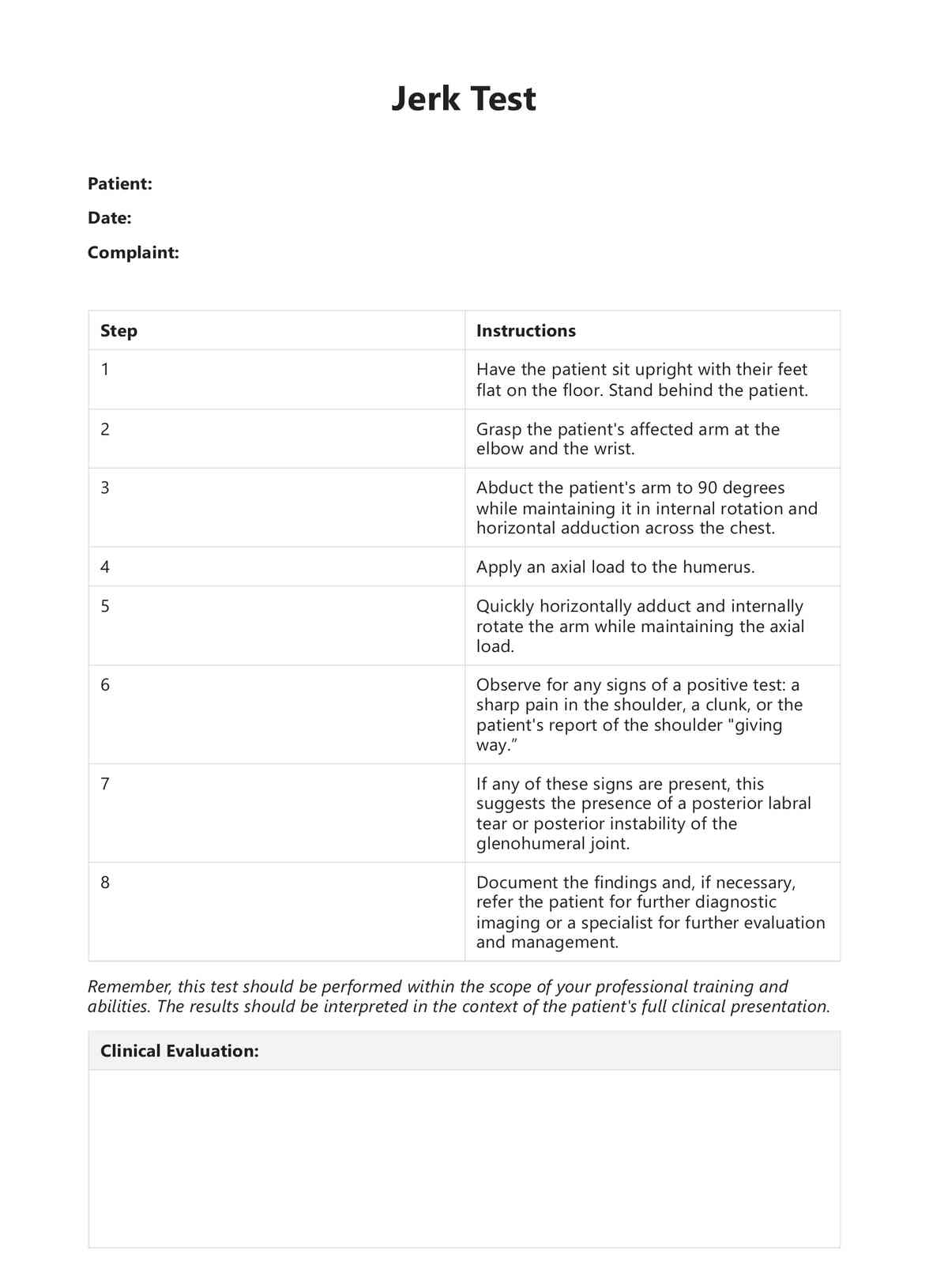
Clinicians developed the Jerk Test as a practical tool for diagnosing shoulder instability, specifically posteroinferior glenohumeral instability.
Jerk Test
Dive deep into the shoulder jerk test. Understand its importance in diagnosing shoulder instability, and grab your free PDF download today.
Use Template
Jerk Test Template
Commonly asked questions
The Jerk Test measures the stability of the glenohumeral joint, specifically detecting posterior labral tears or other causes of posteroinferior instability.
Research supports the Jerk Test as a reliable and valid tool for detecting posterior instability of the glenohumeral joint. Its sensitivity and specificity in identifying posterior labral tears make it valuable for shoulder instability assessment.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











