Pregnant women, often those over 35 or with a family history of genetic conditions by maternal fetal medicine specialists.
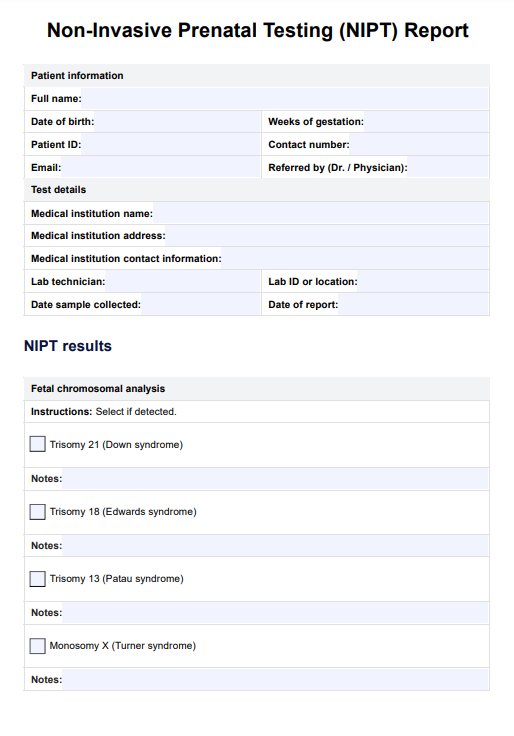
NIPT Blood Test
Discover accurate prenatal screening with our NIPT Test. Get reliable results for genetic conditions early in pregnancy. Download our free PDF guide now.
Use Template
NIPT Blood Test Template
Commonly asked questions
Usually between the 10th and 13th week of pregnancy.
As a screening tool to assess the risk of chromosomal abnormalities.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











