What is a Glucose Tolerance Test?
In the dynamic realm of diagnostic medicine, understanding the nuanced intricacies of various tests is paramount. For healthcare professionals who are perpetually on the quest for precision and accuracy, the Glucose Tolerance Test stands out as a crucial tool, especially in endocrinology and diabetes management.
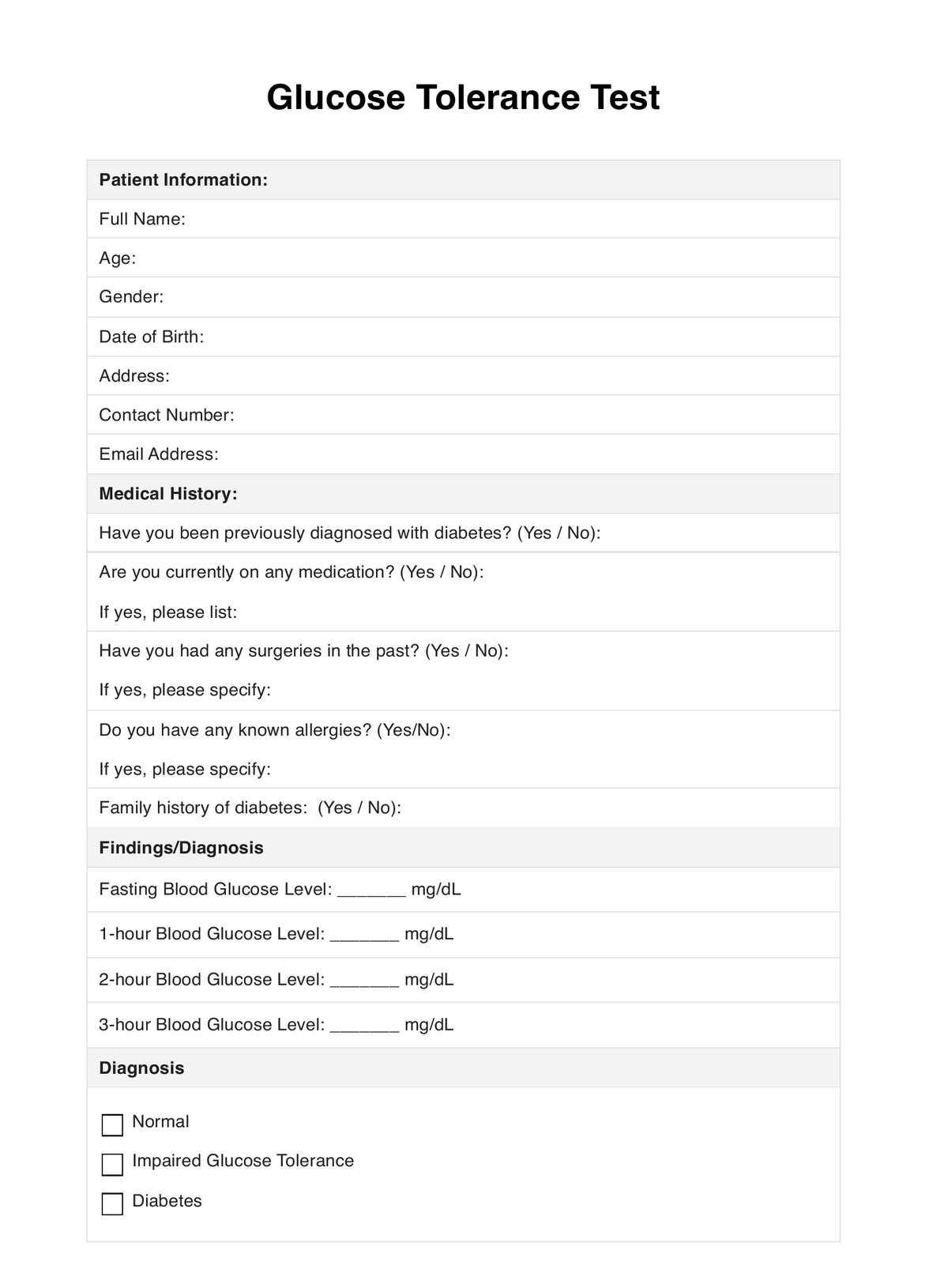
The Glucose Tolerance Test, commonly abbreviated as GTT, is a diagnostic procedure designed to evaluate the body's ability to metabolize and manage glucose. This simple sugar serves as a primary energy source. While glucose is vital for cellular function, its dysregulation can have far-reaching health implications. This is where the GTT enters, offering a window into the body's glucose regulatory mechanisms.
Administered typically after an overnight fast, the test involves the monitored ingestion of a concentrated glucose solution, followed by periodic blood sampling to measure glucose concentrations. These measurements, taken for hours, provide insights into how effectively the body processes the ingested sugar. The patterns observed can indicate normal glucose metabolism, impaired glucose tolerance, or even diabetes.
With the global rise in diabetes cases, early detection and intervention have never been more vital. The GTT is a frontline diagnostic measure, especially for conditions like gestational diabetes, which can impact maternal and fetal health.
Understanding the GTT is more than just knowing the procedure for any healthcare professional. It's about appreciating its role in patient care, its implications for treatment, and its potential to transform lives through early detection and intervention. Dive deeper into this resource to grasp the full scope, nuances, and clinical relevance of the Glucose Tolerance Test.