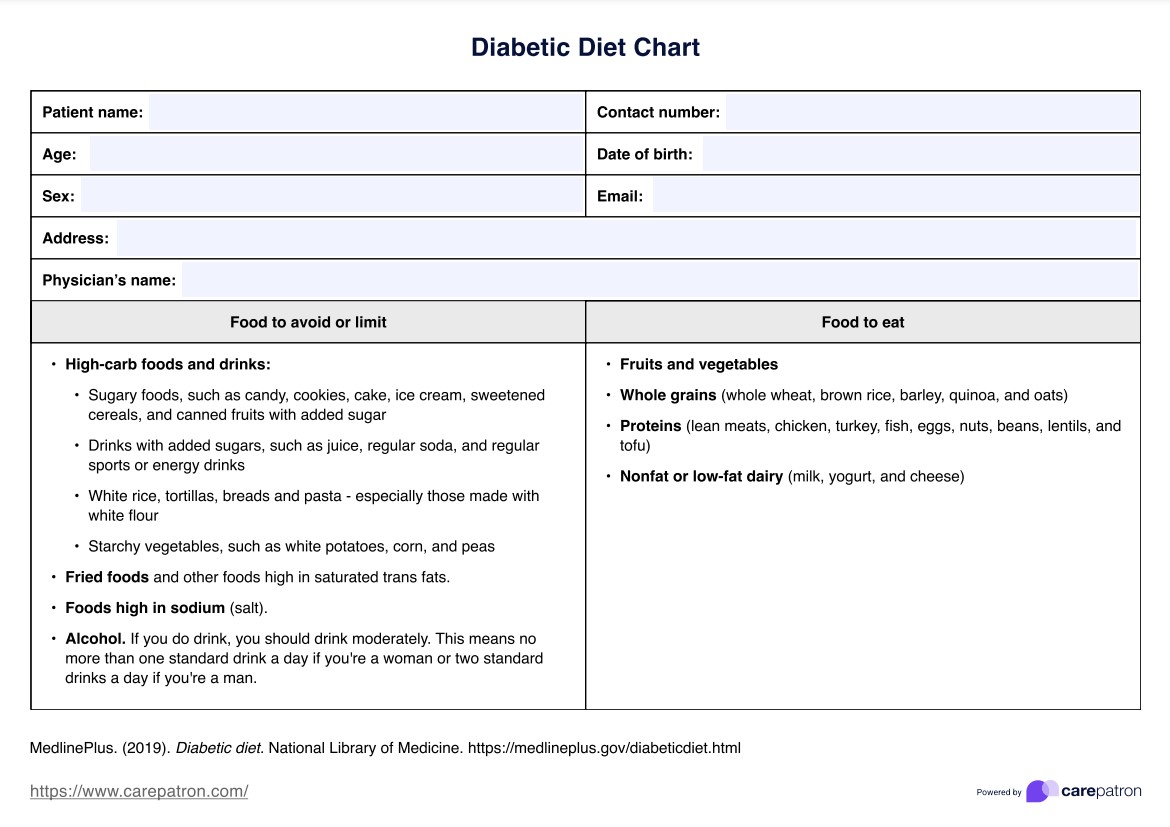
What is a Diabetes Diet Chart?
A Diabetes Diet Chart is a valuable meal-planning tool for your patients with diabetes. It helps them log and monitor their daily food intake and educates users on making healthier food choices by providing a breakdown of the foods they consume daily.
As an integral part of diabetes management, you can employ Diabetes Diet Charts to guide patients toward maintaining a balanced and healthy diet. Properly managing diabetes is crucial, as poor management can result in serious health complications, including heart disease, nerve damage, kidney failure, and vision issues.
By adhering to a diabetes diet plan, individuals can effectively manage their blood sugar levels and mitigate the risk of these complications. This, in turn, helps them maintain stable glucose levels and control other related health conditions.