What is attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)?
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a type of developmental disorder. Those with it tend to have difficulty focusing on something for too long, which happens frequently. They can also become hyperactive and impulsive. It's possible for this developmental disorder to negatively impact a person's daily life and overall mental well-being because of the following:
- They have frequent mood swings.
- They become easily frustrated, and their tempers run hot.
- They become restless and jump from one activity to another.
- They have trouble completing a task or activity, especially boring or repetitive work.
- They have difficulty concentrating.
- They have a hard time prioritizing something.
- They tend to be disorganized.
- They aren't able to plan as well as they'd like (or others would like).
- They get easily stressed and have trouble coping.
- They tend to interrupt others.
- They tend to talk excessively.
- They need to be on the move.
- They have difficulty waiting.
These days, some people are diagnosed with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder during their childhood, so once they hit the adult phase of their life, it's common for them to manage ADHD symptoms and live normally without the disorder disrupting their lives.
However, many people only get a formal diagnosis when they are adults. That's because they were likely unaware of their symptoms, or rather, the symptoms weren't noticeable back then but only began to be noticeable when they were older (like the degree of hyperactivity, impulsivity, etc., being higher than when they were younger).
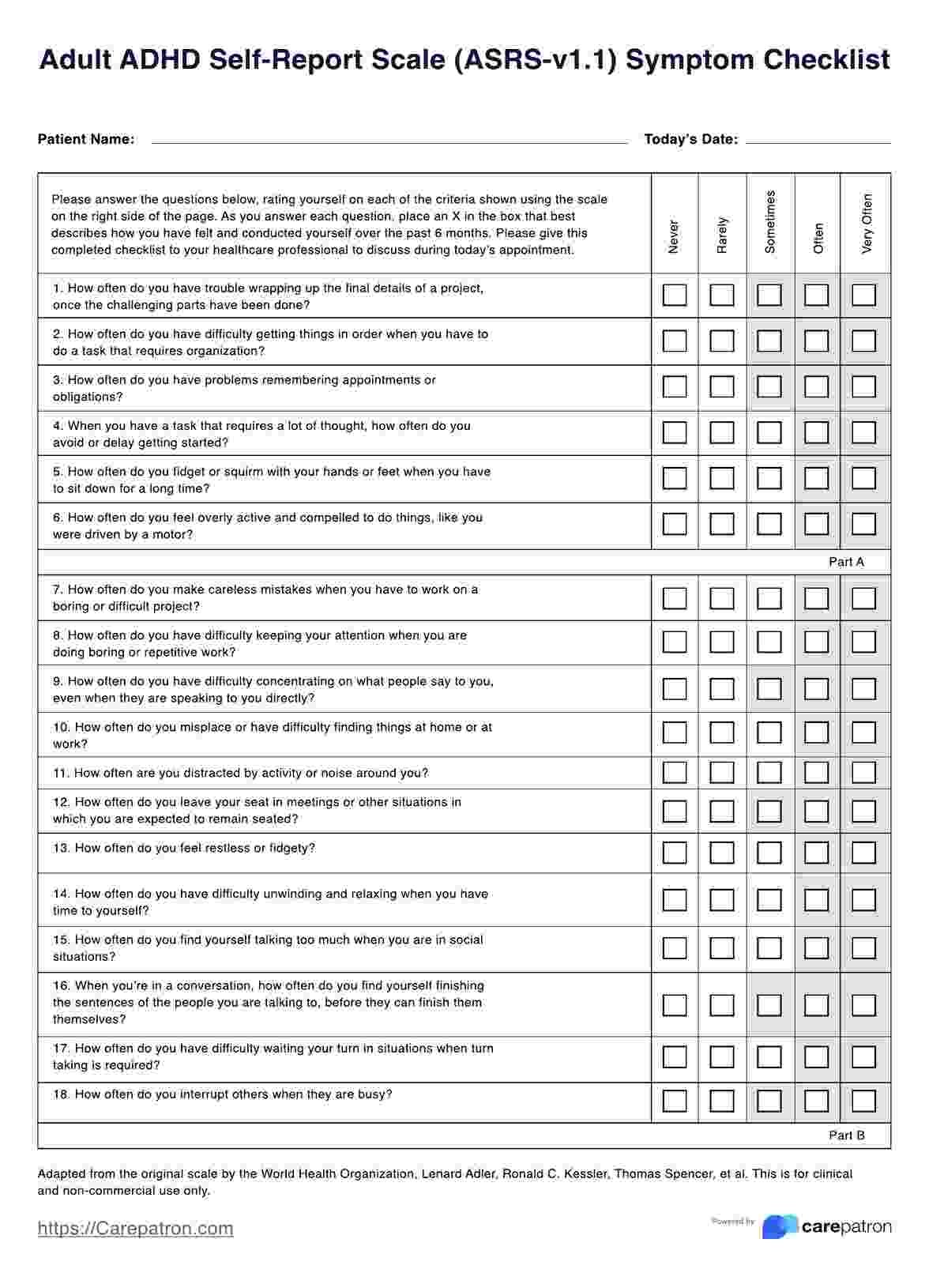
If you're a licensed mental health provider handling a patient who suspects themselves of having ADHD or is suspected by someone close to them, then issue the Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS) to assess them.
Download this Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale and distribute it to clients experiencing symptoms to help diagnose ADHD or other related conditions.