Autoimmune diseases can cause various symptoms, leaving individuals feeling exhausted, achy, and generally unwell. Symptoms may include fatigue, joint pain, muscle aches or weakness, skin rashes, gastrointestinal discomfort, and systemic symptoms such as fever and weight loss. Cognitive impairment or 'brain fog' may also be present in diseases that affect the brain.
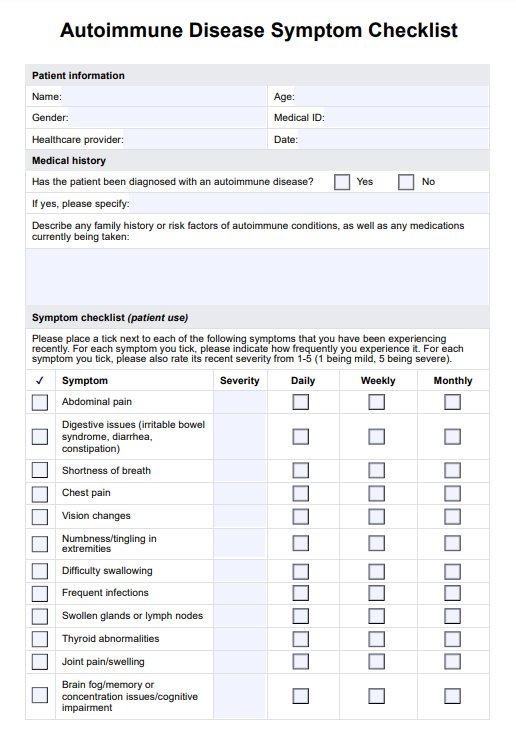
Autoimmune Disease Symptom Checklist
Access Carepatron's free Autoimmune Disease Symptom Checklist, a comprehensive resource for identifying symptoms of autoimmune diseases.
Autoimmune Disease Symptom Checklist Template
Commonly asked questions
While the exact cause is not fully understood, the development of autoimmune diseases is a complex process influenced by genetic factors, environmental factors (e.g., infections, toxins), hormone imbalances, and immune dysregulation. Some types, such as celiac disease, psoriatic arthritis, and Graves' disease (an autoimmune disorder characterized by too much thyroid hormone production), have specific triggers.
While autoimmune diseases cannot typically be cured, they can often be managed effectively. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) help relieve pain. Some individuals find that certain dietary changes, such as following an anti-inflammatory diet or avoiding trigger foods, can help manage symptoms of autoimmune diseases.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











