The cost of foot X-rays can vary depending on location and healthcare provider, but they are generally affordable and often covered by insurance when medically necessary.
Foot Radiograph
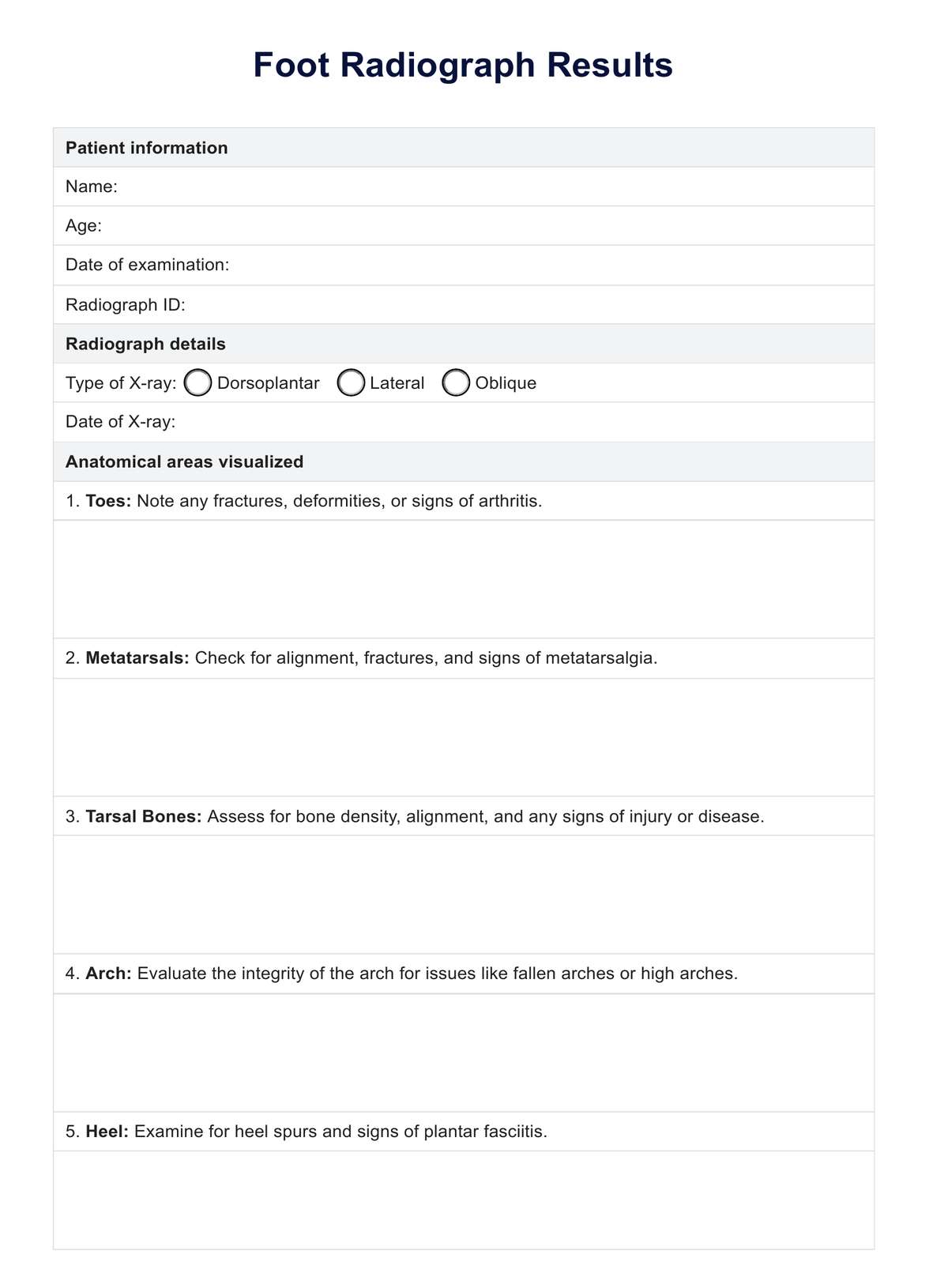
Explore the various uses of foot radiographs, learn how to interpret them, and download our free example of a Foot Radiograph chart
Use Template
Foot Radiograph Template
Commonly asked questions
The process of getting a foot X-ray is painless. Discomfort may arise only if positioning the foot during the X-ray exacerbates an existing injury.
The frequency of foot X-rays depends on the medical condition being monitored or treated. Regular X-rays may be needed for ongoing conditions to assess progress or determine treatment response.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











