When assessing a patient with pneumonia, the nurse should focus on evaluating respiratory status, including vital signs (temperature, respiratory rate, oxygen saturation), breath sounds, and work of breathing. The nurse should also assess for signs of infection, such as fever and chills, and monitor for complications like pleural effusion or respiratory failure. Additionally, the nurse should assess the patient's overall condition, including level of consciousness, hydration status, and ability to cough and clear secretions.
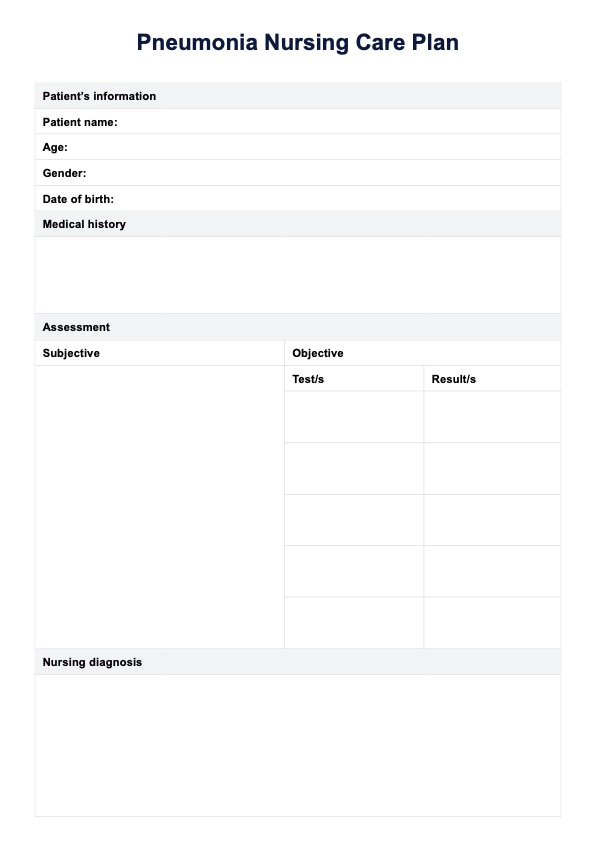
Pneumonia Nursing Care Plan
Confidently manage and monitor pneumonia and its risks through this comprehensive nursing care plan and guide for the delivery of effective and preventive care!
Pneumonia Nursing Care Plan Template
Commonly asked questions
The goal of pneumonia care is to manage symptoms, prevent complications, and promote recovery. This includes providing oxygen therapy, antibiotics if necessary, and supportive care such as hydration and pain management.
Someone with pneumonia typically needs supportive care, including oxygen therapy, antibiotics if necessary, and hydration. They may also require pain management and respiratory support, such as a humidifier or nebulizer. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to provide close monitoring and treatment.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











