Trauma Therapy Techniques
Learn about trauma therapy techniques and how they can help your clients cope with difficult emotions and memories.
Get carepatron free
Commonly asked questions
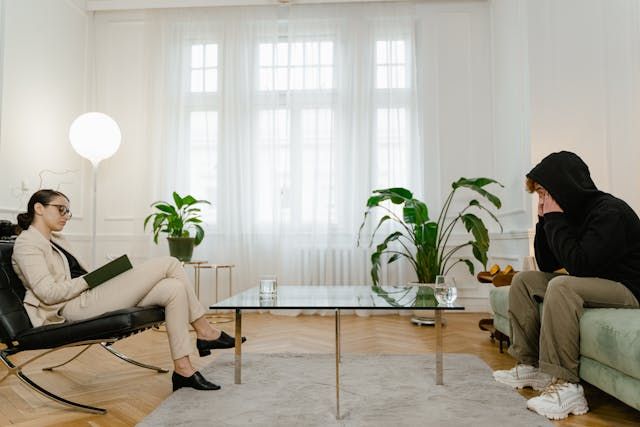
Trauma therapy differs from other types of therapy in that it specifically focuses on helping clients heal from traumatic experiences. It uses various evidence-based techniques to help clients process and make sense of their trauma and recognize and manage triggers associated with the event.
Trauma therapy techniques can help with various issues, such as intrusive memories or flashbacks, avoidance of situations or people associated with the trauma, depression and anxiety, guilt and shame, and feelings of sadness and hopelessness.
Although trauma therapy techniques help manage traumatic experiences, they can come with certain risks and limitations. For example, it may be difficult for the client to open up about their traumatic experience. Additionally, some techniques used in trauma therapy may not be suitable for everyone and could lead to unintended consequences.







