Skin Biopsy
Explore Carepatron’s comprehensive skin biopsy pathology report template, designed for clarity and ease of use, ensuring detailed, accurate biopsy analysis


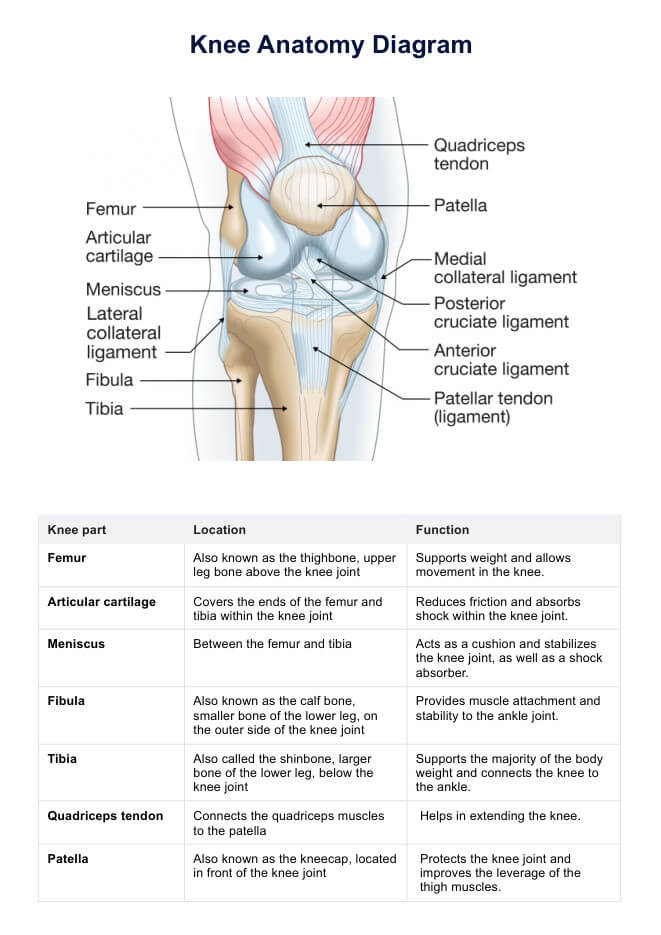
What is a Skin Biopsy?
A skin biopsy is a medical procedure in which a small sample of skin tissue is removed for examination under a microscope. This diagnostic test is essential for identifying various skin conditions, diseases, or abnormalities. The procedure involves taking a tiny portion of the skin, which is then processed and analyzed by pathologists to provide a clear understanding of the patient's skin health.
There are several types of skin biopsy techniques, each suited to different conditions and parts of the body. The most common methods include shave biopsy, where a thin layer of skin is shaved off; punch biopsy, involving a circular tool to remove a small core of skin; and excisional biopsy, where an entire lump or area of abnormal skin is removed. The choice of technique depends on factors such as the size, location, and nature of the skin issue being investigated.
The process of a skin biopsy typically begins with a local anesthetic to numb the area, ensuring the patient’s comfort. The selected skin sample is then carefully removed and preserved in a special solution. It's sent to a pathology lab where it undergoes various analyses, including histological examination.
Skin biopsies play a crucial role in diagnosing a range of dermatological conditions, from benign lesions like moles or warts to more serious issues like skin cancer or inflammatory skin diseases. The results from a skin biopsy can provide definitive diagnoses, helping doctors determine the most effective treatment plan for the patient.
In conclusion, a skin biopsy is a valuable and often necessary procedure in dermatology. It allows for precise diagnosis of skin conditions, guiding appropriate treatment and management. With minimal risks and a relatively simple procedure, it stands as a cornerstone in dermatological diagnostics.
Skin Biopsy Template
Skin Biopsy Example
Utilizing the Skin Biopsy Template
Step 1: Access the template
- Access: Download the template via the provided link below
- Viewing the template: The template can be opened in a standard PDF reader or a word processor, allowing for easy digital interaction and review.
- Printing option: For a physical copy, the template is designed to be printer-friendly. This is useful for face-to-face consultations, discussions with medical teams, or for educating patients about their condition.
Step 2: Familiarize yourself with the Skin Biopsy Template
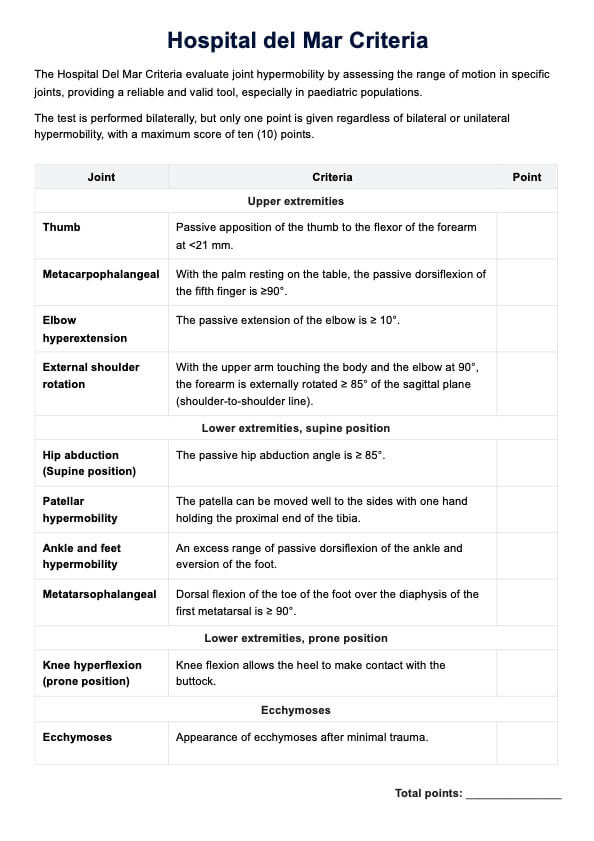
- Review the template to understand various aspects of skin biopsy, such as the types of biopsies, methods of collection, and the significance of each section in the report.
- Identifying key components: Pay attention to essential elements like specimen details, macroscopic and microscopic examination, and diagnosis criteria.
Step 3: Apply the template in clinical practice
- Assessment and diagnosis: Use the template as a comprehensive guide during skin examinations and biopsies. It helps ensure a thorough evaluation of skin lesions or abnormalities.
- Treatment planning: Leverage the diagnostic information in the template to develop personalized care plans. The detailed findings from the biopsy can guide the choice of treatment and management strategies.
- Monitoring progress: The template serves as a tool for tracking the progression of skin conditions and the effectiveness of treatment, as well as identifying any complications that may arise.
How are the results of a Skin Biopsy interpreted?
Interpreting skin biopsy results is a meticulous process undertaken by healthcare professionals, particularly pathologists, to diagnose various skin conditions. After a skin biopsy is performed, the collected skin tissue undergoes a series of examinations in a laboratory. The results from these tests offer critical insights into the nature of the skin lesion or condition being investigated.
The timeline for receiving skin biopsy results can vary, typically ranging from a few days to a couple of weeks. The duration depends on factors like the complexity of the tests, the type of biopsy performed, and the workload of the pathology lab. In urgent cases, the results may be expedited.
When interpreting skin biopsy results, pathologists examine both the macroscopic (visible to the naked eye) and microscopic (cellular level) features of the skin sample. They assess aspects such as the structure, pattern, and type of skin cells, the presence of abnormal cells, and changes in tissue architecture. These observations are crucial in identifying whether the skin biopsy results are normal or indicate a pathological condition.
Abnormal skin biopsy results can reveal a range of conditions, from benign issues like cysts or warts to more serious conditions like skin cancers (e.g., melanoma, basal cell carcinoma). The specific diagnosis is based on the unique cellular patterns and abnormalities identified in the biopsy. For instance, the presence of atypical cells might suggest a precancerous state or cancer, while certain patterns of inflammation can indicate dermatitis or psoriasis.
Healthcare professionals use these results to guide their clinical decisions. The detailed findings from a skin biopsy help in formulating an accurate diagnosis, determining the severity of the condition, and planning the most effective treatment strategy. In summary, skin biopsy results are a pivotal component in dermatological diagnostics, offering essential information for patient care and management.
When are the best times to conduct a skin biopsy?
Deciding the optimal time to conduct a skin biopsy largely depends on the clinical scenario, the type of skin lesion, and the purpose of the biopsy. Understanding when to perform this procedure is key to accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Suspected malignancy
One of the most critical times to conduct a skin biopsy is when there is a suspicion of malignancy, such as in the case of a mole or lesion that has changed in size, shape, color, or texture. Early detection of skin cancers like melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, or squamous cell carcinoma is vital, as early-stage cancers are often more treatable. In these cases, a timely biopsy can be lifesaving.
Diagnostic uncertainty
A skin biopsy is also essential when there is uncertainty in diagnosing a skin condition. Conditions such as psoriasis, eczema, and other inflammatory or infectious skin diseases often present with similar symptoms. A biopsy can provide a definitive diagnosis by revealing characteristic patterns of inflammation or cellular changes unique to each condition.
Monitoring chronic skin conditions
In chronic skin conditions, biopsies may be performed periodically to monitor the disease's progression or response to treatment. This is particularly relevant in conditions like lupus or scleroderma, where the skin changes may have systemic implications.
Evaluating treatment efficacy
For patients undergoing treatment for skin conditions, particularly aggressive or long-term therapies, biopsies may be used to assess the effectiveness of the treatment. This is especially important in conditions where clinical assessment alone may not be sufficient to gauge the response.
In conclusion, the best times to conduct a skin biopsy are when it is crucial for diagnosis, treatment planning, monitoring of a chronic condition, or assessing treatment efficacy. The decision should always be guided by clinical judgment, patient symptoms, and the potential impact on patient care and outcomes.
What are the benefits of a Skin Biopsy?
A skin biopsy is a crucial diagnostic tool in dermatology, offering numerous benefits in understanding and managing various skin conditions. Here’s a breakdown of the key advantages:
Accurate diagnosis
One of the primary skin biopsy benefits is its ability to provide an accurate diagnosis. Skin conditions often present with similar symptoms, making it challenging to identify the specific issue based on a visual examination alone. A biopsy allows for microscopic examination of the skin tissue, enabling pathologists to detect subtle cellular changes and provide a definitive diagnosis. This accuracy is vital for conditions where treatment strategies differ significantly depending on the specific diagnosis.
Early detection of skin cancer
Early detection of skin cancer is another significant benefit. Skin biopsies can identify cancerous changes in moles and other skin lesions, often before they become visually apparent. This early detection is crucial, especially in aggressive cancers like melanoma, where early treatment can significantly improve prognosis.
Guiding treatment
Biopsy results play a crucial role in guiding the treatment plan. By understanding the exact nature of the skin condition, healthcare providers can tailor treatments to be more effective. This is particularly important in cases of chronic or severe skin diseases, where treatment needs to be specific and targeted.
Monitoring disease progression
In chronic skin conditions, biopsies can be used to monitor the disease progression or response to treatment. This ongoing evaluation can be crucial in adjusting treatment plans, ensuring that the patient receives the most effective and appropriate care over time.
Research and advancement
Finally, skin biopsies contribute to research and advancement in dermatology. By studying various skin conditions at a cellular level, researchers can develop better treatments and understand the pathophysiology of skin diseases more deeply.
In summary, the benefits of a skin biopsy are manifold, ranging from providing accurate diagnoses and early cancer detection to guiding treatment and contributing to dermatological research. These advantages underscore the importance of this procedure in modern dermatological practice.
Commonly asked questions
A skin biopsy is a procedure where a small sample of skin is removed and examined under a microscope. It's performed to diagnose skin conditions, including cancers, inflammatory skin diseases, and infections.
There are several methods: punch biopsy (using a circular tool to remove a core), shave biopsy (shaving off the top layer), and excisional biopsy (cutting out the entire area). The method depends on the suspected condition.
Discomfort is usually minimal. The area is numbed with a local anesthetic before the procedure, but there might be some pain or soreness afterward.
Typically, results are available within a few days to two weeks, depending on the complexity of the analysis and the workload of the laboratory.
Abnormal results may indicate skin diseases, such as cancer, psoriasis, or dermatitis. The specific diagnosis depends on the observed cellular changes.