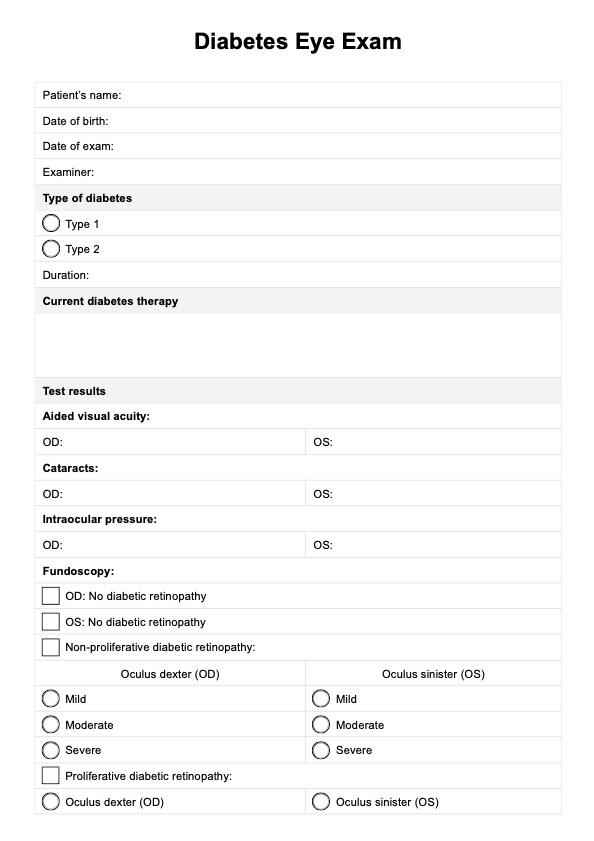
Lung Sounds
Explore how a Lung Sound Chart aids healthcare professionals in identifying and interpreting both normal and abnormal lung sounds, enhancing diagnosis and treatment.


What is a lung sound assessment?
A lung sound assessment is a diagnostic procedure that evaluates and analyzes the sounds produced by the lungs during respiration. It is noninvasive and essential to a physical examination, allowing healthcare professionals to assess the health and functioning of the respiratory system.
During a lung assessment, a healthcare provider uses a stethoscope placed on to the chest wall
to listen to the sounds produced by the lungs, including the expected breath sounds, airflow, vibrations, and any abnormal or adventitious sounds. These sounds can provide important clues about respiratory conditions or abnormalities.
The chest is often examined from the front, sides, and back to perform a thorough assessment. The healthcare professional may advise the patient to take deep breaths, hold their breath, cough, or make certain motions to elicit a certain sound or further evaluate lung function.
A lung sound assessment provides valuable information for diagnosing, monitoring disease progression, and assessing the effectiveness of treatment interventions. It helps healthcare professionals determine the appropriate course of action, such as further diagnostic tests, medication adjustments, or referral to specialists.
Lung Sounds Template
Lung Sounds Example
What is a Lung Sounds Chart?
A Lung Sounds Chart is a visual reference tool used in healthcare settings to assist medical professionals, such as physicians, nurses, and respiratory therapists, in identifying and interpreting various sounds produced by the respiratory system. The chart typically categorizes lung sounds based on their characteristics, helping healthcare providers differentiate between normal and abnormal respiratory sounds.
Healthcare professionals use a Lung Sounds Chart during physical examinations, particularly when auscultating (listening to) a patient's chest with a stethoscope. By referring to this chart, clinicians can enhance their diagnostic skills, make informed assessments, and determine appropriate treatment plans for patients with respiratory conditions.
How to use this Lung Sounds Chart template
The Lung Sounds Chart is an indispensable tool in assessing respiratory health, assisting healthcare professionals in comprehending and analyzing sounds emitted by the lungs during auscultation. Once you have a copy of the chart, follow the next steps to make the most out of the template:
Step 1: Auscultation
During this initial phase, healthcare providers meticulously listen to the sounds generated by the respiratory system using a stethoscope. They strategically position the stethoscope on pre-defined chest areas corresponding to specific lung regions. Note that normal lung sounds occur all around the chest.
Step 2: Identification of sounds
In the subsequent step, professionals differentiate between the various sounds, categorizing them into normal breath sounds (such as tracheal, bronchial, and vesicular) and adventitious sounds (including wheezing, crackles, and rhonchi).
Step 3: Reference to the chart
Healthcare practitioners then refer to the Lung Sounds Chart, cross-referencing the observed sounds with their corresponding locations.
Step 4: Categorization
Systematic categorization follows, wherein the sounds are classified based on their distinctive characteristics. This involves a careful comparison with the detailed descriptions provided on the chart.
Step 5: Interpretation
Interpreting the significance of the identified sounds constitutes a critical aspect of the process. If the healthcare professionals hear normal breathing sounds or vesicular breath sounds, it signifies optimal lung function. Alternatively, abnormal breathing sounds may indicate potential underlying respiratory issues.
Step 6: Decision-making
Armed with a nuanced understanding of lung sounds, healthcare professionals make informed decisions regarding patient care, recommend further diagnostic measures, or formulate appropriate treatment plans based on the identified respiratory nuances.
Interpreting results on the Lung Sounds Chart
Interpreting the results obtained from auscultating lung sounds using a Lung Sounds Chart is crucial for healthcare professionals to make informed clinical decisions. Here's an overview of expected outcomes and their implications:
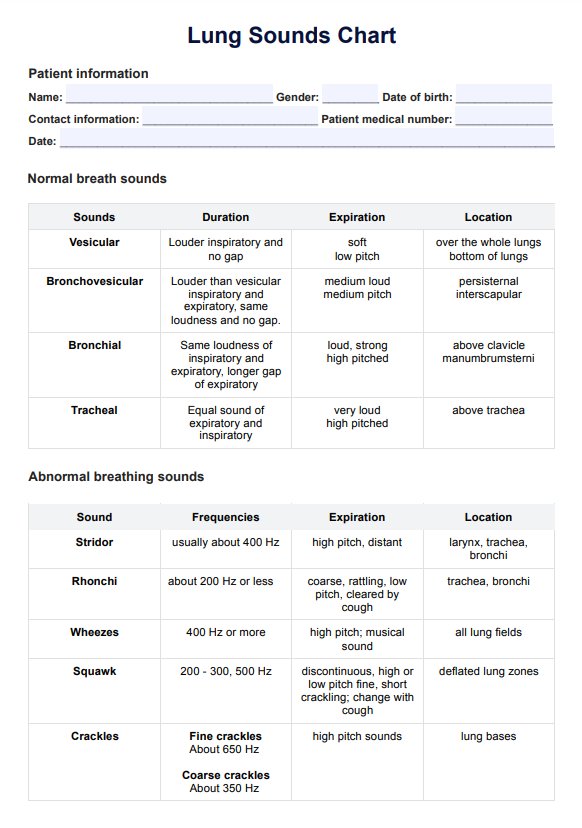
Normal breath sounds
Normal lung sounds are often described as continuous sounds that are clear, crisp, and characterized by air passage through the airways without obstruction. Here are the sounds you can expect depending on the location:
- Tracheal sounds: These high-pitched, loud sounds are heard over the trachea. Their presence indicates normal airflow through the upper airways.
- Bronchial sounds: These are heard near the upper sternum; bronchial breath sounds are medium-pitched and clearer than tracheal sounds. They are normal during expiration.
- Vesicular sounds: Heard over most lung fields, soft, low-pitched sounds. Normal vesicular sounds suggest healthy airflow through the smaller airways and alveoli during inspiration.
Adventitious sounds
If a healthcare professional discovers abnormal breath sounds or adventitious breath sounds like the following, it is encouraged that they examine it further for diagnosis and treatment:
- Wheezing: High-pitched sounds usually heard during expiration. Wheezing can indicate severe trouble breathing, airway constriction, common in asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Crackles: Discontinuous, non-musical sounds heard during inspiration or expiration. Fine crackles may indicate conditions like pneumonia, while coarse crackles can be associated with bronchiectasis or pulmonary fibrosis.
- Rhonchi: Low-pitched, snoring or rattling sounds often heard during expiration. Rhonchi may suggest the presence of mucus or fluid in the airways, which is common in conditions like bronchitis.
- Stridor and squawk: High-pitched, harsh sounds heard during inspiration. Stridor and squawk can be indicative of upper airway obstruction, such as croup or epiglottitis.
Absent or decreased sounds
Other abnormal breathing sounds, such as reduced and absent breath sounds in a specific area, may indicate an obstruction, pleural effusion, or pneumothorax.
Benefits of using a Lung Sound Chart
A lung sound chart enhances respiratory assessments by providing a clear reference for identifying and interpreting both normal and abnormal breath sounds.
Accurate identification of breath sounds
The chart aids in distinguishing between normal and abnormal breath sounds, including tracheal, bronchial, and vesicular breath sounds. By using this tool, healthcare professionals can more accurately identify and categorize the sounds they hear.
Improved diagnostic precision
With the chart, clinicians can better identify abnormal breath sounds, such as wheezing or crackles, which might indicate underlying respiratory conditions like asthma or pneumonia. This improves diagnostic accuracy and ensures appropriate intervention.
Consistent evaluation of lung function
Normal lung sounds occur throughout the chest, and the chart helps in recognizing these typical patterns. It provides a structured approach to evaluating and documenting lung function during physical exams.
Enhanced training and education
The chart is a valuable educational resource for training new healthcare professionals. It helps them understand and differentiate between normal and abnormal breathing sounds, improving their diagnostic skills.
Comprehensive assessment of respiratory health
By allowing clinicians to identify absent breath sounds and other abnormal breathing sounds, the chart supports a thorough assessment of respiratory health. This can guide further diagnostic testing and treatment planning.
Commonly asked questions
Healthcare professionals use the Lung Sounds Chart during physical examinations by auscultating the patient’s chest with a stethoscope. They compare the sounds they hear with those illustrated on the chart to determine if they are normal or indicate potential respiratory issues.
The chart typically includes normal breath sounds like tracheal, bronchial, and vesicular, as well as abnormal sounds such as wheezing, crackles, and rhonchi. Each type is described with characteristics to help differentiate them.
Referencing a Lung Sounds Chart helps ensure accurate identification of respiratory sounds, improves diagnostic precision, and guides appropriate treatment decisions. It provides a structured way to analyze sounds and their implications for the patient’s respiratory health.