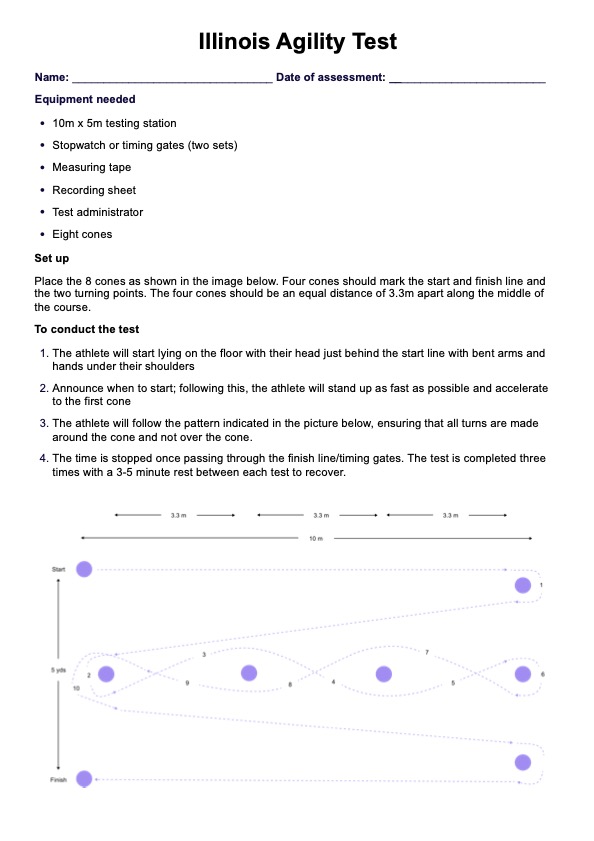
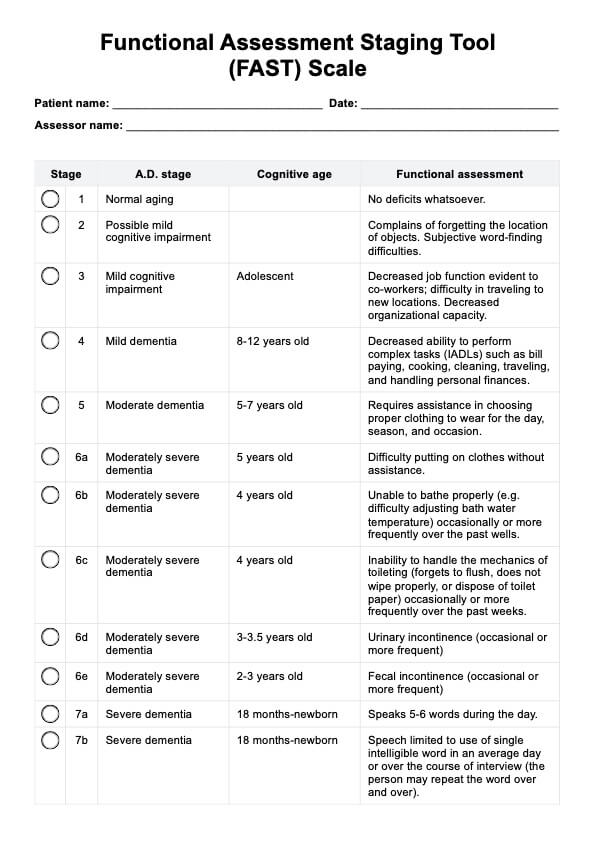
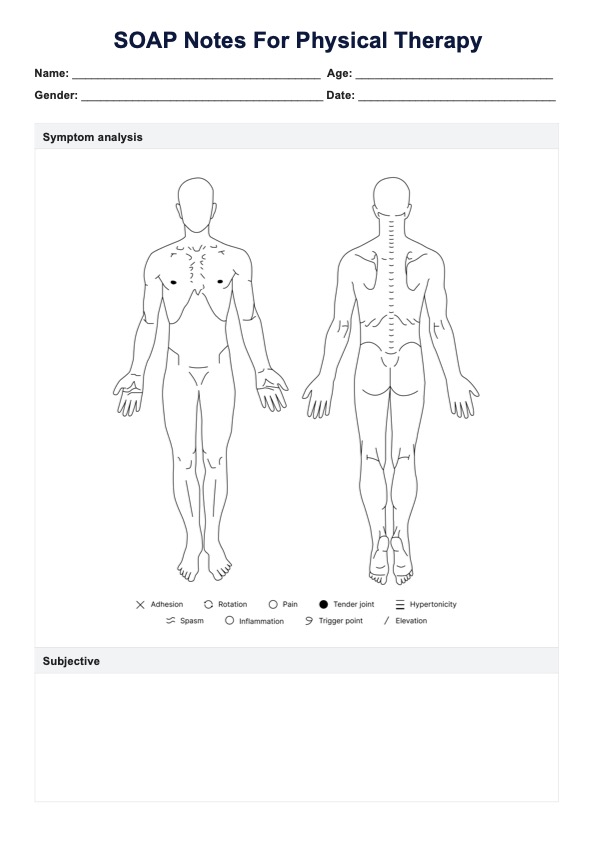
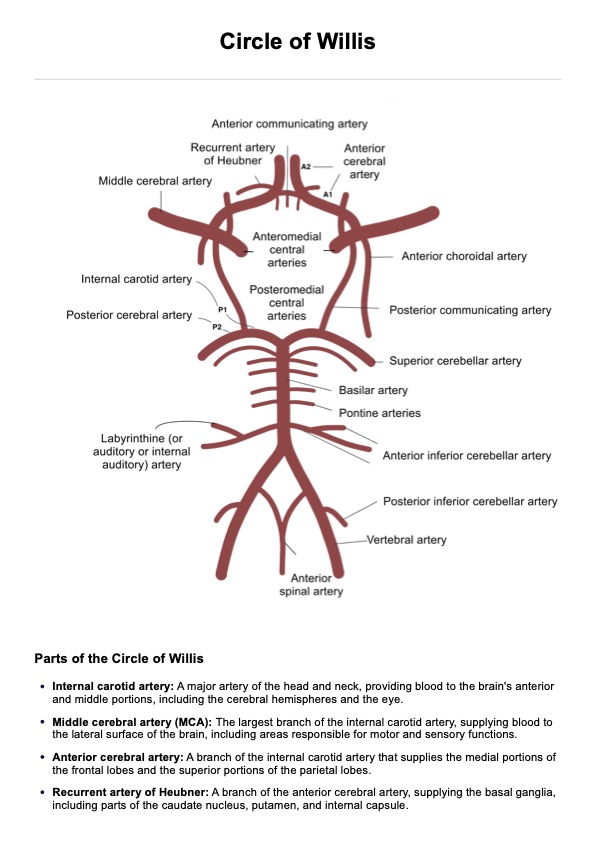
Lead poisoning occurs when lead accumulates in the body, often over months or years. It can cause a range of health issues, from developmental delays in children to memory loss and joint pain in adults. Acute lead poisoning, caused by high levels of exposure in a short time, can lead to severe symptoms like abdominal pain and seizures. Reducing blood lead levels through treatment and stopping exposure is essential for health recovery.

Lead Poisoning Treatment Guidelines
Explore our comprehensive handout, which provides detailed, evidence-based guidelines for the treatment of lead poisoning to support effective care.
Lead Poisoning Treatment Guidelines Template
Commonly asked questions
Lead exposure commonly comes from lead-based paint, contaminated soil, drinking water from lead pipes, and specific workplace materials. In children, lead paint in older homes is a frequent cause of lead toxicity, leading to elevated blood lead levels. Identifying and addressing these sources is critical for disease control and prevention.
Treating lead poisoning begins with identifying and removing the source of exposure. For individuals with elevated blood lead levels, therapies such as chelation may be used to help reduce them. Both childhood lead poisoning and adult lead exposure require monitoring and sometimes medical intervention to prevent long-term health effects.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments