High specific gravity in urine can indicate dehydration or conditions that prevent the kidneys from properly diluting urine, such as renal dysfunction.
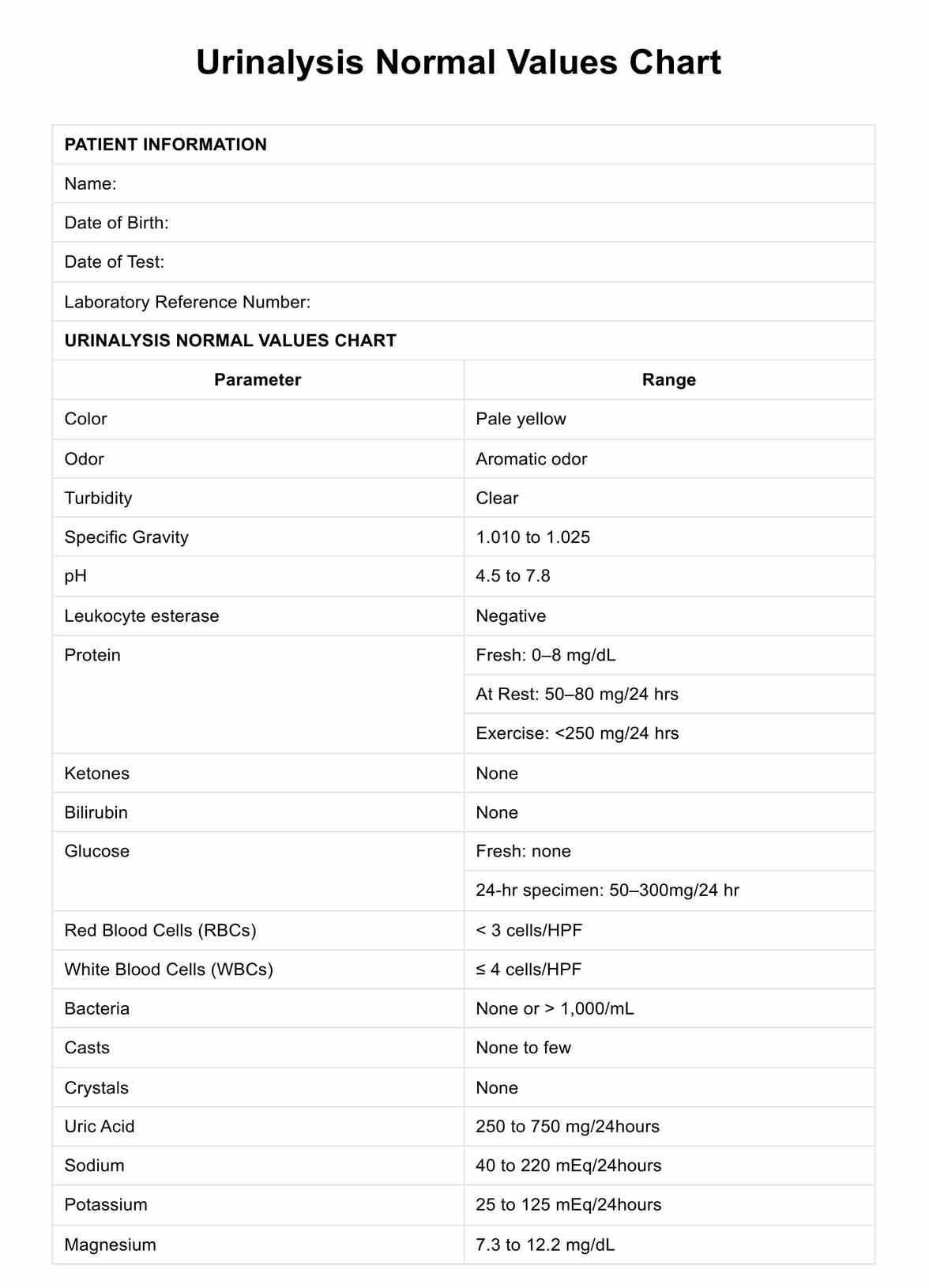
Urinalysis Normal Values Chart
Explore the Urinalysis Normal Values Chart. Understand key health indicators with our comprehensive guide and example. Get your free PDF download now!
Use Template
Urinalysis Normal Values Chart Template
Commonly asked questions
Yes, urinary nitrates can be present in normal urine; however, elevated levels are often associated with urinary tract infections.
Red blood cells in urine can point to various conditions, from benign (like exercise-induced) to serious issues like kidney stones or glomerular disease.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











