That will depend on the patient's procedure, test, or treatment plan, as each position is designed for specific purposes.
Patient Positioning in Bed PDF
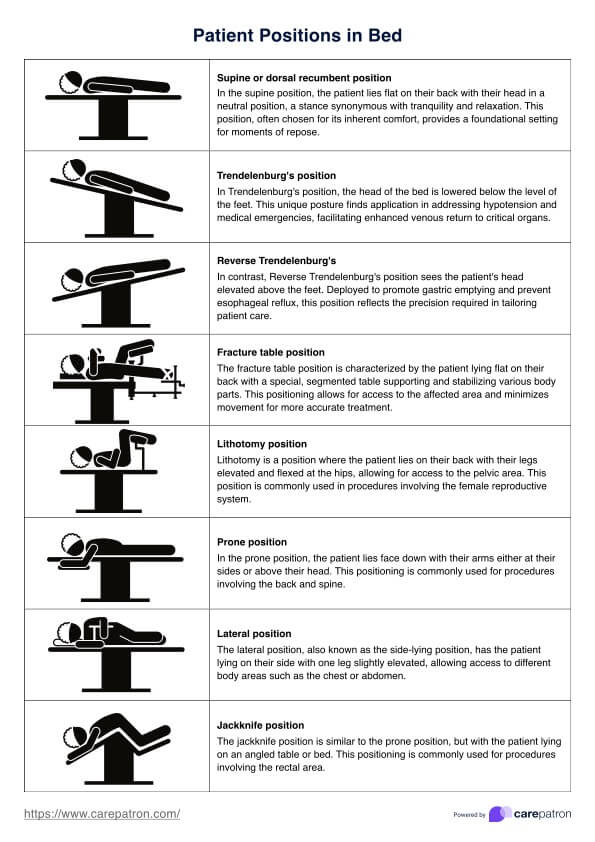
Be well informed about patient positions in bed, their uses, and their importance. Take advantage of our Patient Positioning in Bed PDF cheat sheet!
Use Template
Patient Positioning in Bed PDF Template
Commonly asked questions
Though there are multiple, Fowler's position is the most common, significantly when reducing lower back pain and administering medication.
You can reposition a patient by rolling them towards a side and then back to you. Until you've repositioned them, your patient will be in a specific position based on their capabilities. If this process is challenging, it's best to ask for a helping hand.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











