A normal Foot Posture Index (FPI-6) score ranges from 0 to +5, indicating a balanced foot posture without excessive pronation or supination. This suggests the foot maintains a neutral alignment, distributing weight efficiently during standing and movement. Scores outside this range may indicate a need for further assessment and possible intervention.
Foot Posture Index (FPI-6)
Measure the pronation or supination of a patient’s foot using the Foot Posture Index (FPI-6) to gauge how it can negatively impact their movement.
Foot Posture Index (FPI-6) Template
Commonly asked questions
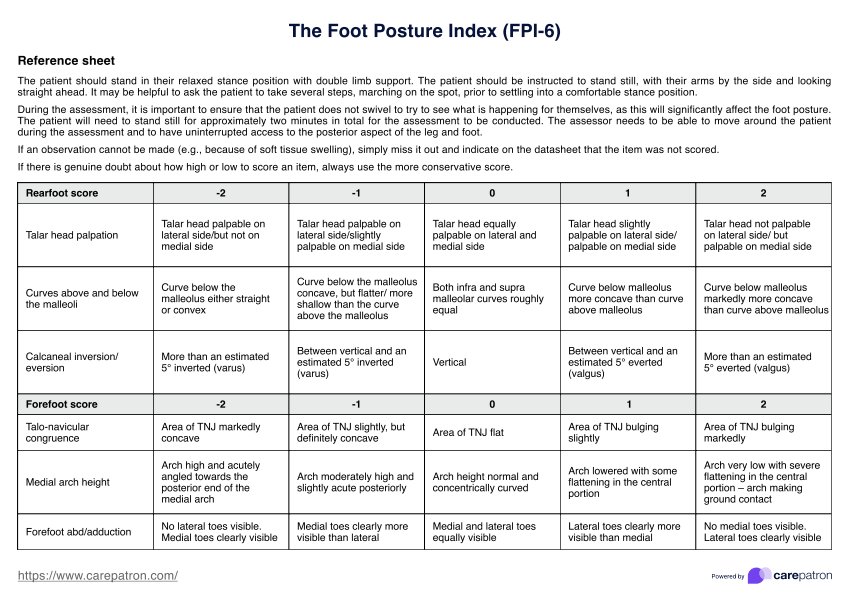
The six criteria assessed in the Foot Posture Index (FPI-6) are talar head palpation, curvature above and below the malleoli, calcaneal inversion/eversion, talo-navicular joint (TNJ) congruence, medial longitudinal arch height, and forefoot abduction/adduction. Each criterion is scored from -2 to +2, helping to classify the foot as supinated, neutral, or pronated.
In foot and ankle research, the Foot Posture Index (FPI-6) is widely used for assessing foot posture. To use the FPI-6, a healthcare professional observes a patient’s standing foot posture while they are in a comfortable stance position. Each of the six criteria is assessed and assigned a score, which is then summed to classify the foot posture as supinated, normal, or pronated. This information helps identify foot type, assess risk factors, and guide treatment decisions in clinical settings.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











